글루코콜티코이드수용체
Glucocorticoid receptorNR3C1(핵수용체 서브패밀리 3, 그룹 C, 멤버 1)이라고도 하는 글루코코르티코이드 수용체(GR, GCR)는 코르티솔 및 기타 글루코코르티코이드가 결합하는 수용체이다.
GR은 신체의 거의 모든 세포에서 발현되며 발달, 신진대사, 면역 반응을 조절하는 유전자를 조절합니다.수용체 유전자는 여러 가지 형태로 발현되기 때문에 신체의 다른 부분에서 많은 다른 (다양성) 효과를 가지고 있다.
글루코콜티코이드가 GR에 결합할 때, 그것의 주요 작용 메커니즘은 유전자 [5][6]전사의 조절이다.결합되지 않은 수용체는 세포의 세포에 존재한다.수용체가 글루코콜티코이드와 결합하면 수용체-글루코콜티코이드 복합체는 두 가지 경로 중 하나를 취할 수 있다.활성화된 GR 복합체는 핵에서 항염증 단백질의 발현을 상향 조절하거나 세포에서 항염증 단백질의 발현을 억제한다(세포에서 핵으로의 다른 전사 인자의 전이를 방지함).
인간에서 GR 단백질은 염색체 5(5q31)[7][8]에 위치한 NR3C1 유전자에 의해 암호화된다.
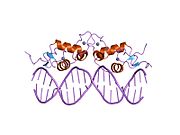
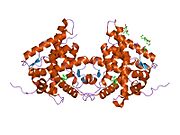
구조.
다른 스테로이드 [9]수용체와 마찬가지로 글루코콜티코이드 수용체는 모듈러[10] 구조이며 다음 도메인(A - F로 표기)을 포함한다.
리간드 결합 및 반응
호르몬이 없는 경우 글루코콜티코이드 수용체(GR)는 히트쇼크단백질 90(hsp90), 히트쇼크단백질 70(hsp70) 및 단백질 FKBP4(FK506결합단백질 4)[11]를 포함한 다양한 단백질과 복합된 세포졸 내에 존재한다.내인성 글루코콜티코이드 호르몬인 코르티솔은 세포막을 통해 세포질로 확산되어 글루코콜티코이드 수용체(GR)에 결합하여 히트 쇼크 단백질을 방출한다.결과적으로 활성화된 형태 GR은 아래에 설명된 대로 두 가지 주요 작용 메커니즘인 트랜스 활성화와 트랜스 억제 메커니즘을 [12][13]가지고 있습니다.
트랜스액티베이션
직접 작용 메커니즘은 수용체의 균질화, 핵으로의 활성 수송을 통한 전위 및 유전자 전사를 활성화하는 특정 DNA 응답 요소에 대한 결합을 포함한다.이 동작 메커니즘은 트랜스액티베이션이라고 불립니다.생물학적 반응은 세포 유형에 따라 달라집니다.
트랜스프레션
활성 GR이 없는 경우 NF-δB 또는 AP-1과 같은 다른 전사 인자는 표적 [14]유전자를 트랜스활성화할 수 있다.그러나 활성화된 GR은 이러한 다른 전사 인자와 복합되어 표적 유전자와 결합하는 것을 방해할 수 있으며, 따라서 NF-δB 또는 AP-1에 의해 일반적으로 상향 조절되는 유전자의 발현을 억제할 수 있다.이 간접적인 작용 메커니즘은 트랜스프레션이라고 불립니다.
임상적 의의
가족성 글루코콜티코이드 [15]저항성의 GR이 비정상입니다.
중추신경계 구조에서 글루코콜티코이드 수용체는 뇌에 대한 내분비 영향, 특히 스트레스 반응의 주요 성분으로 기능하며 신경 내분비 통합을 대표하는 새로운 대표물로 관심을 끌고 있다.이 수용체는 현재 스트레스 인자에 대한 반응으로 보이는 단기 및 장기 적응에 관여하고 있으며 우울증과 외상 후 스트레스 장애(PTSD)[16]의 일부 또는 모든 아형을 포함한 심리적 장애의 이해에 매우 중요할 수 있다.사실, 쿠싱병의 전형적인 기분 조절 장애와 같은 오랜 관찰은 심리 상태를 조절하는 코르티코스테로이드의 역할을 보여준다; 최근의 발전은 신경 [17][18]수준에서 노르에피네프린과 세로토닌과의 상호작용을 보여주었다.
프리클램프시아(임산부에게 흔히 발생하는 고혈압 장애)에서는 이 단백질을 대상으로 하는 miRNA 배열의 수치가 산모의 혈액에서 높아진다.오히려 태반은 이 miRNA를 포함한 엑소좀의 수준을 높여 분자의 번역을 억제할 수 있다.이 정보의 임상적 중요성은 아직 [19]명확하지 않다.
작용제 및 길항제
덱사메타손 및 기타 코르티코스테로이드는 작용제이며, 미페프리스톤 및 케토코나졸은 GR의 길항제이다.
상호 작용
글루코콜티코이드 수용체는 다음 물질과 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 가방1,[20][21]
- CEBPB,[22]
- CREBBP,[23]
- DAP3,[24]
- DAXX,[25]
- HSP90AA1,[24][26][27][28][29][30][31]
- HNRPU,[32]
- MED1,[33][34]
- MED14,[34]
- 미네랄콜티코이드 [35]수용체
- NRIP1,[33][36][37]
- NCOR1,[38][39]
- NCOA1,[33][40]
- NCOA2,[33][41]
- NCOA3,[33][42]
- POU2F1,[43][44]
- RANBP9,[45]
- RELA,[45][46][47]
- SMAD3,[48][49]
- SMARCD1,[42]
- SMARCA4[42][50]
- STAT3,[51][52]
- STAT5B,[53]
- 티오레독신[54]
- TRIM28 [55]및
- 와~[56]
조사.
2022년 6월 28일 발행된 논문은 NR3C1이 ALS의 잠재적 대상 중 하나일 수 있음을 보여주었다.NR3C1은 AI 대응 생물학적 타깃 검출 플랫폼을 사용하여 CNS fALS와 SALS 모두에서 업 레귤레이션된 것으로 밝혀졌다.표적 발견을 통해 [57]ALS를 치료하기 위해 몇 가지 경로와 약물을 추가로 설계할 수 있다.
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
- 막글루코콜티코이드수용체
- 가족성/스포라디성 글루코콜티코이드 내성(크로소스 증후군)
- 선택적 글루코콜티코이드 수용체 작용제(SEGRA)
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000113580 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000024431 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ 루 NZ, 워델 SE, Burnstein한데 KL, Defranco D, 풀러 PJ, Giguere V, 혹버그 RB, 매케이 L, 르누아르 JM, 직경 약 32km. 내셔널 리그, 윌슨은 전자파, 맥도넬 DP, Cidlowski JA(2006년)."국제 약리학의.LXV. 그 약리학과 핵수용체 상과 분류:, 무기질 대사 부신 피질 호르몬, 프로게스테론, 남성 호르몬 글루코 코티 코이드 receptors".Pharmacol 목사 58(4):782–97. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.9. PMID 17132855.S2CID 28626145.[전문 자유].
- ^ Rhen T, Cidlowski JA (October 2005). "Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs". N. Engl. J. Med. 353 (16): 1711–23. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050541. PMID 16236742.
- ^ Hollenberg SM, Weinberger C, Ong ES, Cerelli G, Oro A, Lebo R, Thompson EB, Rosenfeld MG, Evans RM (1985). "Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA". Nature. 318 (6047): 635–41. Bibcode:1985Natur.318..635H. doi:10.1038/318635a0. PMC 6165583. PMID 2867473.
- ^ Francke U, Foellmer BE (May 1989). "The glucocorticoid receptor gene is in 5q31-q32 [corrected]". Genomics. 4 (4): 610–2. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(89)90287-5. PMID 2744768.
- ^ Kumar R, Thompson EB (1999). "The structure of the nuclear hormone receptors". Steroids. 64 (5): 310–9. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(99)00014-8. PMID 10406480. S2CID 18333397.
- ^ Kumar R, Thompson EB (2005). "Gene regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor: structure:function relationship". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 94 (5): 383–94. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.12.046. PMID 15876404. S2CID 25315991.
- ^ Pratt WB, Morishima Y, Murphy M, Harrell M (2006). "Chaperoning of glucocorticoid receptors". Handb Exp Pharmacol. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 172 (172): 111–38. doi:10.1007/3-540-29717-0_5. ISBN 978-3-540-25875-9. PMID 16610357.
- ^ Buckingham JC (2006). "Glucocorticoids: exemplars of multi-tasking". Br J Pharmacol. 147 (Supplement 1): S258–68. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706456. PMC 1760726. PMID 16402112.
- ^ Hayashi R, Wada H, Ito K, Adcock IM (2004). "Effects of glucocorticoids on gene transcription". Eur J Pharmacol. 500 (1–3): 51–62. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.011. PMID 15464020.
- ^ Ray A, Prefontaine KE (January 1994). "Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (2): 752–6. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91..752R. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.2.752. PMC 43027. PMID 8290595.
- ^ Mendonca B, Leite M, de Castro M, Kino T, Elias L, Bachega T, Arnhold I, Chrousos G, Latronico A (2002). "Female pseudohermaphroditism caused by a novel homozygous missense mutation of the GR gene". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87 (4): 1805–9. doi:10.1210/jcem.87.4.8379. PMID 11932321.
- ^ Maletic V, Robinson M, Oakes T, Iyengar S, Ball SG, Russell J (2007). "Neurobiology of depression: an integrated view of key findings". Int J Clin Pract. 61 (12): 2030–40. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01602.x. PMC 2228409. PMID 17944926. [무료 전문]
- ^ Savitz J, Lucki I, Drevets WC (2009). "5HT1A receptor function in Major Depressive Disorder". Prog Neurobiol. 88 (1): 17–31. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.01.009. PMC 2736801. PMID 19428959. [무료 전문]
- ^ Schechter DS, Moser DA, Paoloni-Giacobino A, Stenz A, Gex-Fabry M, Aue T, Adouan W, Cordero MI, Suardi F, Manini A, Sancho Rossignol A, Mermod Day, GermetNR3C1의 메틸화는 폭력 노출 전력이 있는 엄마들 사이의 자녀 분리에 대한 반응으로 모성 PTSD, 육아 스트레스 및 모성 내측 전전두피질 활동과 관련이 있다.심리학 분야의 개척자.온라인 출판물을 보려면 http://www.frontiersin.org/Journal/Abstract.aspx?s=944&name=psychology_for_clinical_settings[permanent dead link]&ART_DOI=10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00690&field=&journalName=Frontiers_in_Psychology&id=139466를 클릭하십시오.
- ^ Salomon C, et al. (2017). "Placental Exosomes as Early Biomarker of Preeclampsia: Potential Role of Exosomal MicroRNAs Across Gestation". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 102 (9): 3182–3194. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00672. PMID 28531338.
- ^ Kullmann M, Schneikert J, Moll J, Heck S, Zeiner M, Gehring U, Cato AC (June 1998). "RAP46 is a negative regulator of glucocorticoid receptor action and hormone-induced apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (23): 14620–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.23.14620. PMID 9603979.
- ^ Schneikert J, Hübner S, Langer G, Petri T, Jäättelä M, Reed J, Cato AC (December 2000). "Hsp70-RAP46 interaction in downregulation of DNA binding by glucocorticoid receptor". EMBO J. 19 (23): 6508–16. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.23.6508. PMC 305849. PMID 11101523.
- ^ Boruk M, Savory JG, Haché RJ (November 1998). "AF-2-dependent potentiation of CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta-mediated transcriptional activation by glucocorticoid receptor". Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (11): 1749–63. doi:10.1210/mend.12.11.0191. PMID 9817600.
- ^ Almlöf T, Wallberg AE, Gustafsson JA, Wright AP (June 1998). "Role of important hydrophobic amino acids in the interaction between the glucocorticoid receptor tau 1-core activation domain and target factors". Biochemistry. 37 (26): 9586–94. doi:10.1021/bi973029x. PMID 9649342.
- ^ a b Hulkko SM, Wakui H, Zilliacus J (August 2000). "The pro-apoptotic protein death-associated protein 3 (DAP3) interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and affects the receptor function". Biochem. J. 349. Pt 3 (3): 885–93. doi:10.1042/bj3490885. PMC 1221218. PMID 10903152.
- ^ Lin DY, Lai MZ, Ann DK, Shih HM (May 2003). "Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) functions as a glucocorticoid receptor co-activator by sequestering Daxx to the PML oncogenic domains (PODs) to enhance its transactivation potential". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (18): 15958–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300387200. PMID 12595526.
- ^ Jibard N, Meng X, Leclerc P, Rajkowski K, Fortin D, Schweizer-Groyer G, Catelli MG, Baulieu EE, Cadepond F (March 1999). "Delimitation of two regions in the 90-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp90) able to interact with the glucocorticosteroid receptor (GR)". Exp. Cell Res. 247 (2): 461–74. doi:10.1006/excr.1998.4375. PMID 10066374.
- ^ Kanelakis KC, Shewach DS, Pratt WB (September 2002). "Nucleotide binding states of hsp70 and hsp90 during sequential steps in the process of glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (37): 33698–703. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204164200. PMID 12093808.
- ^ Hecht K, Carlstedt-Duke J, Stierna P, Gustafsson J, Brönnegârd M, Wikström AC (October 1997). "Evidence that the beta-isoform of the human glucocorticoid receptor does not act as a physiologically significant repressor". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (42): 26659–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.42.26659. PMID 9334248.
- ^ de Castro M, Elliot S, Kino T, Bamberger C, Karl M, Webster E, Chrousos GP (September 1996). "The non-ligand binding beta-isoform of the human glucocorticoid receptor (hGR beta): tissue levels, mechanism of action, and potential physiologic role". Mol. Med. 2 (5): 597–607. doi:10.1007/BF03401643. PMC 2230188. PMID 8898375.
- ^ van den Berg JD, Smets LA, van Rooij H (February 1996). "Agonist-free transformation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human B-lymphoma cells". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 57 (3–4): 239–49. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(95)00271-5. PMID 8645634. S2CID 20582144.
- ^ Stancato LF, Silverstein AM, Gitler C, Groner B, Pratt WB (April 1996). "Use of the thiol-specific derivatizing agent N-iodoacetyl-3-[125I]iodotyrosine to demonstrate conformational differences between the unbound and hsp90-bound glucocorticoid receptor hormone binding domain". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (15): 8831–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.15.8831. PMID 8621522.
- ^ Eggert M, Michel J, Schneider S, Bornfleth H, Baniahmad A, Fackelmayer FO, Schmidt S, Renkawitz R (November 1997). "The glucocorticoid receptor is associated with the RNA-binding nuclear matrix protein hnRNP U". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (45): 28471–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.45.28471. PMID 9353307.
- ^ a b c d e Zilliacus J, Holter E, Wakui H, Tazawa H, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA (April 2001). "Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by 14--3-3-dependent intracellular relocalization of the corepressor RIP140". Mol. Endocrinol. 15 (4): 501–11. doi:10.1210/mend.15.4.0624. PMID 11266503.
- ^ a b Hittelman AB, Burakov D, Iñiguez-Lluhí JA, Freedman LP, Garabedian MJ (October 1999). "Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activation via AF-1-associated proteins". EMBO J. 18 (19): 5380–8. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.19.5380. PMC 1171607. PMID 10508170.
- ^ Savory JG, Préfontaine GG, Lamprecht C, Liao M, Walther RF, Lefebvre YA, Haché RJ (February 2001). "Glucocorticoid receptor homodimers and glucocorticoid-mineralocorticoid receptor heterodimers form in the cytoplasm through alternative dimerization interfaces". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (3): 781–93. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.3.781-793.2001. PMC 86670. PMID 11154266.
- ^ Tazawa H, Osman W, Shoji Y, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA, Zilliacus J (June 2003). "Regulation of subnuclear localization is associated with a mechanism for nuclear receptor corepression by RIP140". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (12): 4187–98. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.12.4187-4198.2003. PMC 156128. PMID 12773562.
- ^ Subramaniam N, Treuter E, Okret S (June 1999). "Receptor interacting protein RIP140 inhibits both positive and negative gene regulation by glucocorticoids". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (25): 18121–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.25.18121. PMID 10364267.
- ^ Stevens A, Garside H, Berry A, Waters C, White A, Ray D (May 2003). "Dissociation of steroid receptor coactivator 1 and nuclear receptor corepressor recruitment to the human glucocorticoid receptor by modification of the ligand-receptor interface: the role of tyrosine 735". Mol. Endocrinol. 17 (5): 845–59. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0320. PMID 12569182.
- ^ Schulz M, Eggert M, Baniahmad A, Dostert A, Heinzel T, Renkawitz R (July 2002). "RU486-induced glucocorticoid receptor agonism is controlled by the receptor N terminus and by corepressor binding". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 26238–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203268200. PMID 12011091.
- ^ Kucera T, Waltner-Law M, Scott DK, Prasad R, Granner DK (July 2002). "A point mutation of the AF2 transactivation domain of the glucocorticoid receptor disrupts its interaction with steroid receptor coactivator 1". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 26098–102. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204013200. PMID 12118039.
- ^ Bledsoe RK, Montana VG, Stanley TB, Delves CJ, Apolito CJ, McKee DD, Consler TG, Parks DJ, Stewart EL, Willson TM, Lambert MH, Moore JT, Pearce KH, Xu HE (July 2002). "Crystal structure of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain reveals a novel mode of receptor dimerization and coactivator recognition". Cell. 110 (1): 93–105. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00817-6. PMID 12151000. S2CID 6955342.
- ^ a b c Hsiao PW, Fryer CJ, Trotter KW, Wang W, Archer TK (September 2003). "BAF60a mediates critical interactions between nuclear receptors and the BRG1 chromatin-remodeling complex for transactivation". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (17): 6210–20. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.17.6210-6220.2003. PMC 180928. PMID 12917342.
- ^ Préfontaine GG, Walther R, Giffin W, Lemieux ME, Pope L, Haché RJ (September 1999). "Selective binding of steroid hormone receptors to octamer transcription factors determines transcriptional synergism at the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (38): 26713–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.38.26713. PMID 10480874.
- ^ Préfontaine GG, Lemieux ME, Giffin W, Schild-Poulter C, Pope L, LaCasse E, Walker P, Haché RJ (June 1998). "Recruitment of octamer transcription factors to DNA by glucocorticoid receptor". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (6): 3416–30. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.6.3416. PMC 108923. PMID 9584182.
- ^ a b Rao MA, Cheng H, Quayle AN, Nishitani H, Nelson CC, Rennie PS (December 2002). "RanBPM, a nuclear protein that interacts with and regulates transcriptional activity of androgen receptor and glucocorticoid receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (50): 48020–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209741200. PMID 12361945.
- ^ Nissen RM, Yamamoto KR (September 2000). "The glucocorticoid receptor inhibits NFkappaB by interfering with serine-2 phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain". Genes Dev. 14 (18): 2314–29. doi:10.1101/gad.827900. PMC 316928. PMID 10995388.
- ^ Caldenhoven E, Liden J, Wissink S, Van de Stolpe A, Raaijmakers J, Koenderman L, Okret S, Gustafsson JA, Van der Saag PT (April 1995). "Negative cross-talk between RelA and the glucocorticoid receptor: a possible mechanism for the antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids". Mol. Endocrinol. 9 (4): 401–12. doi:10.1210/mend.9.4.7659084. PMID 7659084.
- ^ Li G, Wang S, Gelehrter TD (October 2003). "Identification of glucocorticoid receptor domains involved in transrepression of transforming growth factor-beta action". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (43): 41779–88. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.631.7318. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305350200. PMID 12902338. S2CID 950035.
- ^ Song CZ, Tian X, Gelehrter TD (October 1999). "Glucocorticoid receptor inhibits transforming growth factor-beta signaling by directly targeting the transcriptional activation function of Smad3". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (21): 11776–81. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9611776S. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.21.11776. PMC 18362. PMID 10518526.
- ^ Wallberg AE, Neely KE, Hassan AH, Gustafsson JA, Workman JL, Wright AP (March 2000). "Recruitment of the SWI-SNF chromatin remodeling complex as a mechanism of gene activation by the glucocorticoid receptor tau1 activation domain". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (6): 2004–13. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.6.2004-2013.2000. PMC 110817. PMID 10688647.
- ^ Lerner L, Henriksen MA, Zhang X, Darnell JE (October 2003). "STAT3-dependent enhanceosome assembly and disassembly: synergy with GR for full transcriptional increase of the alpha 2-macroglobulin gene". Genes Dev. 17 (20): 2564–77. doi:10.1101/gad.1135003. PMC 218150. PMID 14522952.
- ^ Zhang Z, Jones S, Hagood JS, Fuentes NL, Fuller GM (December 1997). "STAT3 acts as a co-activator of glucocorticoid receptor signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (49): 30607–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.49.30607. PMID 9388192.
- ^ Stöcklin E, Wissler M, Gouilleux F, Groner B (October 1996). "Functional interactions between Stat5 and the glucocorticoid receptor" (PDF). Nature. 383 (6602): 726–8. Bibcode:1996Natur.383..726S. doi:10.1038/383726a0. PMID 8878484. S2CID 4356272.
- ^ Makino Y, Yoshikawa N, Okamoto K, Hirota K, Yodoi J, Makino I, Tanaka H (January 1999). "Direct association with thioredoxin allows redox regulation of glucocorticoid receptor function". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (5): 3182–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.5.3182. PMID 9915858.
- ^ Chang CJ, Chen YL, Lee SC (October 1998). "Coactivator TIF1beta interacts with transcription factor C/EBPbeta and glucocorticoid receptor to induce alpha1-acid glycoprotein gene expression". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (10): 5880–7. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.10.5880. PMC 109174. PMID 9742105.
- ^ Wakui H, Wright AP, Gustafsson J, Zilliacus J (March 1997). "Interaction of the ligand-activated glucocorticoid receptor with the 14-3-3 eta protein". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (13): 8153–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.13.8153. PMID 9079630.
- ^ Pun, Frank W.; Liu, Bonnie Hei Man; Long, Xi; Leung, Hoi Wing; Leung, Geoffrey Ho Duen; Mewborne, Quinlan T.; Gao, Junli; Shneyderman, Anastasia; Ozerov, Ivan V.; Wang, Ju; Ren, Feng (2022). "Identification of Therapeutic Targets for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using PandaOmics – An AI-Enabled Biological Target Discovery Platform". Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 14. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2022.914017/full#h4. ISSN 1663-4365.
추가 정보
- Adcock IM, Ito K (2000). "Molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid actions". Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease. 55 (3): 256–66. PMID 10948677.
- Chikanza IC (2002). "Mechanisms of corticosteroid resistance in rheumatoid arthritis: a putative role for the corticosteroid receptor beta isoform". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 966 (1): 39–48. Bibcode:2002NYASA.966...39C. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04200.x. PMID 12114257. S2CID 85100496.
- Neeck G, Kluter A, Dotzlaw H, Eggert M (2002). "Involvement of the glucocorticoid receptor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 966 (1): 491–5. Bibcode:2002NYASA.966..491N. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04252.x. PMID 12114309. S2CID 5106644.
- Yudt MR, Cidlowski JA (2003). "The glucocorticoid receptor: coding a diversity of proteins and responses through a single gene". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (8): 1719–26. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0106. PMID 12145329.
- Torrego A, Pujols L, Picado C (2003). "[Response to glucocorticoid treatment in asthma. The role of alpha and beta isoforms of the glucocorticoid receptor]". Arch. Bronconeumol. 38 (9): 436–40. doi:10.1016/S0300-2896(02)75258-7. PMID 12237016.
- Bray PJ, Cotton RG (2003). "Variations of the human glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1): pathological and in vitro mutations and polymorphisms". Hum. Mutat. 21 (6): 557–68. doi:10.1002/humu.10213. PMID 12754700. S2CID 26191891.
- Kino T, Pavlakis GN (2004). "Partner molecules of accessory protein Vpr of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1". DNA Cell Biol. 23 (4): 193–205. doi:10.1089/104454904773819789. PMID 15142377.
- Lu NZ, Cidlowski JA (2004). "The origin and functions of multiple human glucocorticoid receptor isoforms". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1024 (1): 102–23. Bibcode:2004NYASA1024..102L. doi:10.1196/annals.1321.008. PMID 15265776. S2CID 36368837.
- Kino T, Chrousos GP (2004). "Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 accessory protein Vpr: a causative agent of the AIDS-related insulin resistance/lipodystrophy syndrome?". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1024 (1): 153–67. Bibcode:2004NYASA1024..153K. doi:10.1196/annals.1321.013. PMID 15265780. S2CID 23655886.
- Andersen JL, Planelles V (2005). "The role of Vpr in HIV-1 pathogenesis". Curr. HIV Res. 3 (1): 43–51. doi:10.2174/1570162052772988. PMID 15638722.
- Le Rouzic E, Benichou S (2006). "The Vpr protein from HIV-1: distinct roles along the viral life cycle". Retrovirology. 2 (1): 11. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-2-11. PMC 554975. PMID 15725353.
- Muthumani K, Choo AY, Premkumar A, et al. (2006). "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vpr-regulated cell death: insights into mechanism". Cell Death Differ. 12 (Suppl 1): 962–70. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401583. PMID 15832179.
- Zhou J, Cidlowski JA (2005). "The human glucocorticoid receptor: one gene, multiple proteins and diverse responses". Steroids. 70 (5–7): 407–17. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2005.02.006. PMID 15862824. S2CID 24272404.
- Chrousos GP, Kino T (2006). "Intracellular glucocorticoid signaling: a formerly simple system turns stochastic". Sci. STKE. 2005 (304): pe48. doi:10.1126/stke.3042005pe48. PMID 16204701. S2CID 23148406.
- Plotkin LL, Labutin AL, Lebedev LV, et al. (1975). "[Balloon probe for the removal of emboli and thrombi]". Meditsinskaya Tekhnika (3): 42–3. PMID 1152650.
- Subramaniam M, Colvard D, Keeting PE, et al. (1993). "Glucocorticoid regulation of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, and proto-oncogenes in normal human osteoblast-like cells". J. Cell. Biochem. 50 (4): 411–24. doi:10.1002/jcb.240500410. PMID 1469072. S2CID 21381419.
- Scherrer LC, Pratt WB (1992). "Association of the transformed glucocorticoid receptor with a cytoskeletal protein complex" (PDF). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41 (3–8): 719–21. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90411-B. hdl:2027.42/30199. PMID 1562545. S2CID 43672040.
- Cadepond F, Gasc JM, Delahaye F, et al. (1992). "Hormonal regulation of the nuclear localization signals of the human glucocorticosteroid receptor". Exp. Cell Res. 201 (1): 99–108. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(92)90352-9. PMID 1612132.
- Hurley DM, Accili D, Stratakis CA, et al. (1991). "Point mutation causing a single amino acid substitution in the hormone binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor in familial glucocorticoid resistance". J. Clin. Invest. 87 (2): 680–6. doi:10.1172/JCI115046. PMC 296359. PMID 1704018.
- Encío IJ, Detera-Wadleigh SD (1991). "The genomic structure of the human glucocorticoid receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (11): 7182–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(20)89627-6. PMID 1707881.
외부 링크
- 인간단백질참조데이터베이스
- 미국 국립 의학 도서관(MeSH)의 글루코콜티코이드+수용체
- 팩터북 GR
- PDBe-KB의 UniProt: P04150(글루코코르티코이드 수용체)에 있는 PDB에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 구조 정보의 개요.