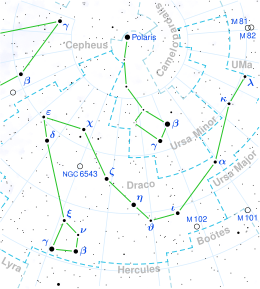
람다 드라코니스
Lambda Draconis| 관측 데이터 Epoch J2000.0 이쿼녹스 J2000.0(ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| 별자리 | 드라코 |
| 우측 상승 | 11h 31m 24.22075s[1] |
| 탈위임 | +69° 19′ 51.8696″[1] |
| 겉보기 크기 (V) | +3.85[2] |
| 특성. | |
| 진화 단계 | 점근성 거목[3] |
| 스펙트럼형 | M0III-IIIa Ca1[4] |
| U-B색지수 | +1.97[2] |
| B-V색지수 | +1.62[2] |
| 변수형 | 느린 불규칙.[5] |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 방사 속도 (Rv) | +6.58±0.30km[6]/s |
| 고유 운동 (μ) | RA: −40.97[1]mas/yr Dec.: −19.19[1]mas/yr |
| 시차 (π) | 9.79 ± 0.15[1] 마스 |
| 거리 | 333 ± 5 리 (102 ± 2 pc) |
| 절대치수 (MV) | −1.14±0.033[7] |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 미사 | 1.7[8] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 71[9] R☉ |
| 루미도 | 834[10] L☉ |
| 표면 중력 (log g) | 1.10±0.05[11] cgs |
| 온도 | 3,958K[10] |
| 기타 지정 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바드 | 자료 |
람다 드라코니스(Lam Dra, 약칭 Lam Dra, λ Dra) 역시 지아우사르 /ˈdʒɔzzzrr/[13][14]로 명명된 드라코 북쪽의 원형 별자리에 [15]있는 주황색 붉은[16] 별이다.육안으로 볼 수 있는 시각적 크기는 +3.85이다.[2]지구에서 볼 수 있는 연간 시차 변화 9.79 mas를 바탕으로, [1]이 별은 태양으로부터 약 333광년 떨어진 곳에 위치해 있다.
이것은 M0III-IIIA Ca1이라는 별의 분류를 가진 점근거성 가지에[3] 있는 진화된 붉은 거성 별이다.[4]약 1,100일의 주기성을 가진 느리게 나타나는 변광성이다.[5]사지 다크닝 보정 후 측정된 각 직경은 6.43±0.07 mas이다.[17]항성의 추정 거리에서, 이것은 태양의 반경의 약 53배의 물리적 크기를 산출한다.[9]태양 질량의 1.7배로[8] 추정되며 광구에서 유효온도 3,958K로 태양 광도의 834배를 방출하고 있다.[10]
명명법
λ 드라코니스(Lambda Draconis에 라티네이즈)는 스타의 바이엘 명칭이다.
그것은 전통적인 이름인 기아우사르[18](기안파르, 기안사르, 기아우사르라고도 표기)와 주자를 가지고 있었다.국제천문연맹은 2016년 항성명 작업반(WGSN)[19]을 조직해 항성의 적절한 명칭을 분류하고 표준화했다.WGSN은 2017년 2월 1일 이 별의 지아우사르라는 이름을 승인했으며, 현재는 IAU가 승인한 별명 목록에 포함되어 있다.[14]
In Chinese, 紫微右垣 (Zǐ Wēi Yòu Yuán), meaning Right Wall of Purple Forbidden Enclosure, refers to an asterism consisting of Lambda Draconis, Alpha Draconis, Kappa Draconis, 24 Ursae Majoris, 43 Camelopardalis, Alpha Camelopardalis and BK Camelopardalis.[20]따라서 람다 드라코니스의 중국식 이름 자체가 紫垣垣 ((Z w Wii Yuu Yuan Sann, 영어: Purple Buarded Enclosure의 오른쪽 벽의 제3성)[21]이며, 이는 제1차 장관을 의미한다.[22]上輔(Shungfǔ)은 R.H.알렌에 의해 상푸나 샤우푸로 서구화되었다.[23]
네임스케이크
USS Giansar(AK-111)는 이 별의 이름을 딴 미국 해군 크레이터급 화물선이다.
참조
- ^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c d Johnson, H. L.; et al. (1966), "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars", Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, 4 (99): 99, Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ^ a b Eggen, O. J. (1992). "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun". The Astronomical Journal. 104: 275. Bibcode:1992AJ....104..275E. doi:10.1086/116239.
- ^ a b Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989), "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 71: 245, Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K, doi:10.1086/191373.
- ^ a b Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2007), Combined General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS4.2), retrieved 2016-09-30.
- ^ Famaey, B.; et al. (2009), "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants,. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 498 (2): 627–640, arXiv:0901.0934, Bibcode:2009A&A...498..627F, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698, S2CID 18739721.
- ^ Park, Sunkyung; et al. (2013), "Wilson-Bappu Effect: Extended to Surface Gravity", The Astronomical Journal, 146 (4): 73, arXiv:1307.0592, Bibcode:2013AJ....146...73P, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/146/4/73, S2CID 119187733.
- ^ a b Gondoin, P. (December 1999), "Evolution of X-ray activity and rotation on G-K giants", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 352: 217–227, Bibcode:1999A&A...352..217G.
- ^ a b Lang, Kenneth R. (2006), Astrophysical formulae, Astronomy and astrophysics library, vol. 1 (3rd ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 3-540-29692-1. 반지름(R*)은 다음을 통해 제공된다.
- ^ a b c McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343–357, arXiv:1208.2037, Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352.
- ^ Takagi, Yuhei; et al. (June 2011), "Age Determinations of Early-M Type Pre-Main Sequence Stars Using a High-Resolution Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Method", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 63 (3): 677–684, Bibcode:2011PASJ...63..677T, doi:10.1093/pasj/63.3.677.
- ^ "lam Dra". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint : 포스트스크립트(링크) - ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- ^ a b "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ^ Moore, Patrick (2013), The Observer's Year: 366 Nights of the Universe, The Patrick Moore Practical Astronomy Series, Springer Science & Business Media, p. 285, ISBN 978-1447136132
- ^ Richichi, A.; et al. (February 2005), "CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 431 (2): 773–777, Bibcode:2005A&A...431..773R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042039.
- ^ Kaler, James B., "Giausar", stars.astro.illinois.edu, retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ^ "International Astronomical Union IAU". www.iau.org. Retrieved 2017-03-31.
- ^ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金.Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (중국어로) 香港太館 - - 研究中中照表 홍콩 우주박물관 웨이백머신(Wayback Machine)에 2008-10-25년 보관.2010년 11월 23일 전화 접속.
- ^ 홍콩 우주박물관 웨이백머신(Wayback Machine)에 2008-09-24년 보관된 중국 스타 지역의 영자 용어집, 별자리 및 별 이름.2010년 11월 23일 전화 접속.
- ^ Allen, Richard Hinckley (1963), Star Names — Their Lore and Meaning: Draco, the Dragon, retrieved 2017-05-28.