아리에티스 엡실론
Epsilon Arietis| 관측 데이터 에폭 J2000 이쿼녹스 J2000 | |
|---|---|
| 별자리 | 양자리 |
| 우측 상승 | 02h 59m 12.72536s[1] |
| 탈위임 | +21° 20′ 25.5575″[1] |
| 겉보기 크기 (V) | 4.63[2] (5.2/5.5)[3] |
| 특성. | |
| 스펙트럼형 | A2 Vs + A2 Vs[4] |
| U-B색지수 | +0.08[2] |
| B-V색지수 | +0.04[2] |
| R-I 색지수 | 0.02 |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 방사 속도 (Rv) | +0.9 ± 0.9[5] km/s |
| 고유 운동 (μ) | RA: -13.74[1]mas/yr Dec.: -5.12마스[1]/yr |
| 시차 (π) | 9.81 ± 0.79[1] 마스 |
| 거리 | 330 ± 30 리 (105 ± 8pc) |
| 궤도[6] | |
| 기간 (P) | 704.111±1.778 yr |
| 반주축 (a) | 2.174±0.035″ |
| 편심성 (e) | 0.317±0.006 |
| 기울기 (i) | 84.2±0.8° |
| 노드의 경도 (Ω) | 25.6±0.7° |
| 페리아스트론 신기원을 이루다 (T) | 704.111±1.778 |
| 페리아스트론의 인수 (ω) (2차) | 162.1±1.0° |
| 세부 사항 | |
| ε 아리 A | |
| 미사 | 2.4[6] M☉ |
| 회전 속도 (v sin i) | 초속[4] 60km/s |
| ε 아리 B | |
| 미사 | 2.4[6] M☉ |
| 회전 속도 (v sin i) | 초속[4] 60km/s |
| 기타 지정 | |
| ε Ari A: HD 18520, HR 888, SAO 75673 | |
| ε Ari B: HD 18519, HR 887. | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바드 | ari |
| ε 아리 A | |
| ε 아리 B | |
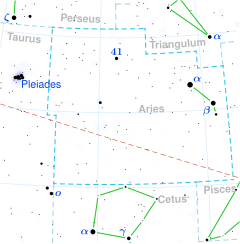
엡실론 아리에티스(Epsilon Arietis, ) Arietis)는 북양자리 별자리에 있는 시각적 이진[8] 별 시스템을 위한 바이엘 명칭이다.두 성분이 너무 가까이 붙어 있어 망원경 없이 해결할 수 없지만, 겉보기 크기가 4.63이며[2] 육안으로 볼 수 있다.연간 시차 변화량 9.81 mas로,[1] 이 시스템까지의 거리는 330광년(100파섹)으로 추정할 수 있으며, 30광년의 오차범위를 주거나 가질 수 있다.다크 클라우드 MBM12 뒤에 위치한다.[6]
이 쌍의 더 밝은 부재는 겉보기 크기가 5.2이다.[3]209.2° ± 0.3°[8]의 위치 각도를 따라 밝은 구성 요소로부터 1.426 ± 0.010 아크의 각이 분리될 때, 크기는 5.5 동반이다.[3]두 별 모두 A2 Vs('[4]s' 접미사는 스펙트럼 내 흡수선이 뚜렷하게 좁다는 것을 나타낸다)의 별 분류가 A형 주계열성이다.2009년 'Ap, HgMn, Am 별의 카탈로그'에서 두 별의 분류는 A3Ti로 티타늄이 비정상적으로 풍부한 Ap 별임을 나타낸다.[3]오차 한계 내에서 이들의 예상 회전 속도는 60 km/s에서 동일한 것으로 간주된다.[4]
이름
이 항성계는 Δ 아리, ζ 아리, π 아리, ρ3 아리와 함께 벨리인 알바인의 이중인 알부랭( (أبain)이었다.[9]According to the catalogue of stars in the Technical Memorandum 33-507 - A Reduced Star Catalog Containing 537 Named Stars, Al Buṭain were the title for five stars :δ Ari as Botein, π Ari as Al Buṭain I, ρ3 Ari as Al Buṭain II, ε Ari as Al Buṭain III and ζ Ari as Al Buṭain IV[10]
중국 천문학에서 엡실론 아리에티스(Arietis)는 Tso Kang(광동어 左更zogang, 만다린 발음 zuǒgēng)의 일부일 수도 있다.[11][12]
참조
- ^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c d Eggen, Olin J. (November 1963), "Luminosities, colors, and motions of the brightest A-type stars", Astronomical Journal, 68: 697, Bibcode:1963AJ.....68..697E, doi:10.1086/109198.
- ^ a b c d Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (May 2009), "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 498 (3): 961–966, Bibcode:2009A&A...498..961R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810788.
- ^ a b c d e Royer, F.; et al. (October 2002), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars in the northern hemisphere. II. Measurement of v sin i", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 393: 897–911, arXiv:astro-ph/0205255, Bibcode:2002A&A...393..897R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020943, S2CID 14070763.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006), "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system", Astronomy Letters, 32 (11): 759–771, arXiv:1606.08053, Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G, doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065, S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b c d Rica, Francisco (April 2012), "Orbital Elements for BU 741 AB, STF 333 AB, BU 920 and R 207", Journal of Double Star Observations, 8 (2): 127–139, Bibcode:2012JDSO....8..127R.
- ^ "eps Ari". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2012-08-05.
- ^ a b Scardia, M.; Prieur, J.-L.; Pansecchi, L.; Argyle, R. W.; Basso, S.; Sala, M.; Ghigo, M.; Koechlin, L.; Aristidi, E. (January 2007), "Speckle observations with PISCO in Merate - III. Astrometric measurements of visual binaries in 2005 and scale calibration with a grating mask", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 374 (3): 965–978, Bibcode:2007MNRAS.374..965S, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11206.x.
- ^ Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc. p. 83. ISBN 0-486-21079-0. Retrieved 2010-12-12.
- ^ Jack W. Roads - 1971년 11월 15일 캘리포니아 공과대학교 제트 추진 연구소의 명명된 별 537개를 포함한 기술 비망록 33-507-A 감소된 별 카탈로그
- ^ Chevalier, S., and Tsuchihashi, P., (1911): "Catalogue d'Étoiles fixes, observés a Pekin sous l'Empereur Kien Long (Qianlong (Chien-Lung)), XVIIIe siecle", Annales de l'Observatoire Astronomique de Zô-Sé.
- ^ 伊世同 (Yi Shi Tong) (1981): 『中西対照恒星図表』科学出版社.(in Chinese)