스피란톨
Spilanthol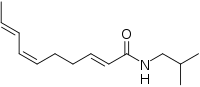 | |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| 선호 IUPAC 이름 (2E,6Z,8E)-N-(2-메틸프로필)데카-2,6,8-트리엔아미드 | |
| 기타 이름 아피닌 | |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
펍켐 CID | |
| 유니 | |
CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| 특성. | |
| C14H23NO | |
| 어금질량 | 221.344 g·2014−1 |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하고, 표준 상태(25°C [77°F], 100 kPa)의 재료에 대한 데이터가 제공된다. | |
| Infobox 참조 자료 | |
Spilanthol은 Acmella Oleracea에서 분리된 지방산 아미드다.[1] 식물의 국소마취 성질을 담당하는 것으로 생각된다.[2]
스피란톨은 사람의 피부와 입안의 볼 안쪽 안감(부칼 점막)에 스며들어 국소적으로 뿐만 아니라 전신 약리학적 농도를 유발한다.[4]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ Ramsewak, RS; Erickson, AJ; Nair, MG (1999). "Bioactive N-isobutylamides from the flower buds of Spilanthes acmella". Phytochemistry. 51 (6): 729–32. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00101-6. PMID 10389272.
- ^ Spelman, Kevin; Depoix, Delphine; McCray, Megan; Mouray, Elisabeth; Grellier, Philippe (2011). "The Traditional Medicine Spilanthes acmella, and the Alkylamides Spilanthol and Undeca-2E-ene-8,10-diynoic Acid Isobutylamide, Demonstrate in Vitro and in Vivo Antimalarial Activity". Phytotherapy Research. 25 (7): 1098–101. doi:10.1002/ptr.3395. PMC 3374932. PMID 22692989.
- ^ Boonen, Jente; Baert, Bram; Roche, Nathalie; Burvenich, Christian; De Spiegeleer, Bart (2010). "Transdermal behaviour of the N-alkylamide spilanthol (affinin) from Spilanthes acmella (Compositae) extracts". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 127 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.046. PMID 19808085.
- ^ Boonen, Jente; Baert, Bram; Burvenich, Christian; Bondeel, Phillip; De Saeger, Sarah; De Spiegeleer, Bart (2010). "LC-MS profiling of N-alkylamides in Spilanthes acmella extract and the transmucosal behaviour of its main bio-active spilanthol". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 53 (3): 243–249. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.02.010. PMID 20227845.


