EIF4E
EIF4E| EIF4E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 식별자 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 에일리어스 | EIF4E, 진핵생물 번역 개시인자 4E, AUTS19, CBP, EIF4E1, EIF4EL1, EIF4F, eIF-4E | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 외부 ID | OMIM: 133440 MGI: 95305 HomoloGene: 123817 GenCards: EIF4E | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 맞춤법 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 종. | 인간 | 마우스 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 엔트레즈 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 앙상블 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 유니프로트 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq(mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq(단백질) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 장소(UCSC) | Chr 4: 98.88 ~98.93 Mb | Chr 3: 138.23 ~138.27 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed 검색 | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 위키데이터 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
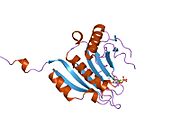
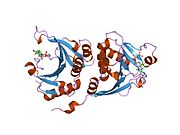
eIF4E로도 알려진 진핵생물 번역 개시인자 4E는 EIF4E [5][6]유전자에 의해 인간에게 암호화되는 단백질이다.
구조 및 기능
대부분의 진핵 세포 mRNA는 7-메틸-구아노신 5-프라임 캡 구조인 m7GppPX(여기서 X는 모든 뉴클레오티드)에 의해 5' 말단에서 차단된다.이 구조는 향상된 번역 효율성, 스플라이싱, mRNA 안정성 및 RNA 핵 수출을 포함한 여러 세포 과정에 관여합니다.eIF4E는 mRNA의 캡 구조로 리보솜을 유도하는 진핵생물 번역 개시 인자이다.자유 형태 및 eIF4F 사전 개시 [7]복합체의 일부로 존재하는 24-kD 폴리펩타이드입니다.거의 모든 세포 mRNA는 단백질로 변환되기 위해 eIF4E를 필요로 한다.eIF4E 폴리펩타이드는 진핵생물 번역 장치의 속도 제한 성분이며 진핵생물 단백질 합성의 mRNA-리보솜 결합 단계에 관여한다.
eIF4F의 다른 서브유닛은 ATPase 및 RNA 헬리케이스 활성을 갖는 47-kD 폴리펩타이드(eIF4A)[8]와 220-kD 비계 폴리펩타이드(eIF4G)[9][10][11]이다.
일부 바이러스는 eIF4E 결합 부위가 제거되고 바이러스가 eIF4E 없이 단백질을 번역할 수 있는 방식으로 eIF4G를 차단한다.또한 일부 세포 단백질, 가장 주목할 만한 것은 열충격 단백질은 번역되기 위해 eIF4E를 필요로 하지 않는다.바이러스와 세포 단백질 모두 RNA의 내부 리보솜 진입 부위를 통해 이를 달성한다.
규정
eIF4E는 상대적으로 존재감이 낮은 개시 인자이므로 eIF4E는 전사 [12]제어의 잠재적 대상이다.eIF4E의 조절은 전사,[13] 인산화 및 억제 단백질의 세 가지 메커니즘을 통해 달성될 수 있다.
a. 유전자 발현에 의한 eIF4E 조절
eIF4E 전사 조절을 담당하는 메커니즘은 완전히 이해되지 않았습니다.그러나 여러 보고서에 따르면 세포 [14]주기 동안 myc 수준과 eIF4E mRNA 수준 간의 상관관계가 있습니다.이러한 관계의 기초는 eIF4E [15]유전자의 프로모터 영역에서 두 개의 myc 결합 부위(CACGTG E box repeats)의 특성화에 의해 더욱 확립되었다.이 배열 모티브는 myc에 대한 다른 생체 내 표적과 공유되며 eIF4E의 E박스 반복 변이가 프로모터 영역을 비활성화하여 발현을 감소시킨다.
b. 인산화에 의한 eIF4E의 조절
호르몬, 성장인자, 세포 증식을 촉진하는 유사분열물질과 같은 자극은 또한 [16]eIF4E를 인산화함으로써 번역률을 높인다.eIF4E 인산화와 번역률이 항상 상관관계가 있는 것은 아니지만, 세포주기 전반에 걸쳐 일관된 eIF4E 인산화 패턴이 관찰된다. 여기서 낮은 인산화율은 G 및0 M 단계에서 나타나고 높은 인산화율은 [17]G 및 S1 단계에서 나타난다.이러한 증거는 세린 잔기 209에 대한 인산화 작용이 캡 mRNA에 대한 eIF4E의 친화력을 증가시킬 수 있음을 시사하는 eIF4E의 결정 구조에 의해 더욱 뒷받침된다.
c. 억제단백질에 의한 eIF4E 조절
eIF4F 복합체의 조립은 eIF4E 결합 단백질(4E-BPs)로 알려진 단백질에 의해 억제되며, 이는 캡의존성 [13]번역을 차단하는 작은 열안정 단백질이다.비인산화 4E-BP는 eIF4E와 강하게 상호작용하여 번역을 방지하고, 인산화 4E-BP는 eIF4E에 약하게 결합하므로 [18]번역을 방해하지 않는다.또한 4E-BPs의 결합은 [19]eIF4E에서의 Ser209의 인산화 억제를 한다.
암에서 eIF4E의 역할
암에서 eIF4E의 역할은 Lazaris-Karatzas 등이 eIF4E를 과도하게 발현하면 섬유아세포의 [20]종양 유발 변형을 일으킨다는 사실을 발견한 이후 확립되었다.이러한 초기 관찰 이후, 많은 그룹이 이러한 결과를 다른 [21]세포줄로 반복했습니다.그 결과, eIF4E 활동은 유방암, 폐암, 전립선암을 포함한 여러 암에 관련된다.실제로 전이성 인간 종양의 전사 프로파일링은 eIF4E가 일관되게 상향 [22]조절되는 것으로 알려진 뚜렷한 대사 특성을 밝혀냈다.
FMRP는 EIF4E 바인딩을 통해 변환을 억제합니다.
연약한 X 정신지체단백질(FMR1)은 eIF4E의 결합을 통해 특정 mRNA의 번역을 조절하는 역할을 한다.FMRP는 CYFIP1을 바인드함으로써 동작합니다.CYFIP1은 EIF4EBP3, EIF4EBP1, EIF4EBP2 등의 4E-BP에서 발견된 것과 구조적으로 유사한 도메인에서 eIF4e를 직접 바인드합니다.FMRP/CYFIP1 복합체는 변환에 필요한 eIF4E-eIF4G 상호작용을 방지하도록 결합한다.FMRP/CYFIP1/eIF4E 상호작용은 mRNA의 존재에 의해 강화된다.특히, BC1 RNA는 FMRP와 CYFIP1 사이의 최적의 상호작용을 가능하게 한다. RNA-BC1은 비번역성 수지상 mRNA이며, 이것은 FMRP가 특정 표적 mRNA와 관련되도록 결합한다. BC1은 FMRPapse SynRNA [23]및 MRNA에서의 상호작용을 조절하는 기능을 할 수 있다.
또한 FMRP는 변환을 억제하기 위해 특정 mRNA에 CYFIP1을 채용할 수 있습니다.FMRP-CYFIP1 변환 억제제는 뉴런의 자극에 의해 조절된다.시냅스 자극 증가는 eIF4E와 CYFIP1의 해리를 초래하여 [23]번역의 시작을 가능하게 했다.
상호 작용
EIF4E는 다음과 상호작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000151247 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000028156 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Pelletier J, Brook JD, Housman DE (August 1991). "Assignment of two of the translation initiation factor-4E (EIF4EL1 and EIF4EL2) genes to human chromosomes 4 and 20". Genomics. 10 (4): 1079–82. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90203-Q. PMID 1916814.
- ^ Jones RM, MacDonald ME, Branda J, Altherr MR, Louis DN, Schmidt EV (May 1997). "Assignment of the human gene encoding eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (EIF4E) to the region q21-25 on chromosome 4". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 23 (3): 221–223. doi:10.1007/BF02721373. PMID 9330633. S2CID 10683455.
- ^ Sonenberg N, Rupprecht KM, Hecht SM, Shatkin AJ (September 1979). "Eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein: purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose-coupled m7GDP". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 76 (9): 4345–9. Bibcode:1979PNAS...76.4345S. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.9.4345. PMC 411571. PMID 291969.
- ^ Hutchins AP, Roberts GR, Lloyd CW, Doonan JH (2004). "In vivo interaction between CDKA and eIF4A: a possible mechanism linking translation and cell proliferation". FEBS Lett. 556 (1–3): 91–4. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01382-6. PMID 14706832. S2CID 35343626.
- ^ Hsieh AC, Ruggero D (11 August 2010). "Targeting Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E (eIF4E) in Cancer". Clinical Cancer Research. 16 (20): 4914–4920. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0433. PMC 7539621. PMID 20702611.
- ^ Rychlik W, Domier LL, Gardner PR, Hellmann GM, Rhoads RE (February 1987). "Amino acid sequence of the mRNA cap-binding protein from human tissues". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 84 (4): 945–9. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84..945R. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.4.945. PMC 304336. PMID 3469651.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: eIF4E Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E".
- ^ Duncan, R.; Milburn, S. C.; Hershey, J. W. (1987-01-05). "Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (1): 380–388. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)75938-9. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 3793730.
- ^ a b Richter, Joel D.; Sonenberg, Nahum (2005-02-03). "Regulation of cap-dependent translation by eIF4E inhibitory proteins". Nature. 433 (7025): 477–480. Bibcode:2005Natur.433..477R. doi:10.1038/nature03205. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 15690031. S2CID 4347657.
- ^ Rosenwald, I. B.; Rhoads, D. B.; Callanan, L. D.; Isselbacher, K. J.; Schmidt, E. V. (1993-07-01). "Increased expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factors eIF-4E and eIF-2 alpha in response to growth induction by c-myc". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (13): 6175–6178. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.6175R. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.13.6175. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 46890. PMID 8327497.
- ^ Jones, R. M.; Branda, J.; Johnston, K. A.; Polymenis, M.; Gadd, M.; Rustgi, A.; Callanan, L.; Schmidt, E. V. (September 1996). "An essential E box in the promoter of the gene encoding the mRNA cap-binding protein (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E) is a target for activation by c-myc". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (9): 4754–4764. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.9.4754. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 231476. PMID 8756633.
- ^ Morley, S. J.; Traugh, J. A. (1990-06-25). "Differential stimulation of phosphorylation of initiation factors eIF-4F, eIF-4B, eIF-3, and ribosomal protein S6 by insulin and phorbol esters". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (18): 10611–10616. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)86990-3. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 2191953.
- ^ Bonneau, A. M.; Sonenberg, N. (1987-08-15). "Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (23): 11134–11139. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)60935-4. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 3038908.
- ^ Peter, Daniel; Igreja, Cátia; Weber, Ramona; Wohlbold, Lara; Weiler, Catrin; Ebertsch, Linda; Weichenrieder, Oliver; Izaurralde, Elisa (2015-03-19). "Molecular architecture of 4E-BP translational inhibitors bound to eIF4E". Molecular Cell. 57 (6): 1074–1087. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.017. ISSN 1097-4164. PMID 25702871.
- ^ Whalen, S. G.; Gingras, A. C.; Amankwa, L.; Mader, S.; Branton, P. E.; Aebersold, R.; Sonenberg, N. (1996-05-17). "Phosphorylation of eIF-4E on serine 209 by protein kinase C is inhibited by the translational repressors, 4E-binding proteins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (20): 11831–11837. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.20.11831. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8662663.
- ^ Lazaris-Karatzas, A.; Montine, K. S.; Sonenberg, N. (1990-06-07). "Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap". Nature. 345 (6275): 544–547. Bibcode:1990Natur.345..544L. doi:10.1038/345544a0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 2348862. S2CID 4366949.
- ^ Pelletier, Jerry; Graff, Jeremy; Ruggero, Davide; Sonenberg, Nahum (2015-01-15). "TARGETING THE eIF4F TRANSLATION INITIATION COMPLEX: A CRITICAL NEXUS FOR CANCER DEVELOPMENT". Cancer Research. 75 (2): 250–263. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2789. ISSN 0008-5472. PMC 4299928. PMID 25593033.
- ^ Ramaswamy, Sridhar; Ross, Ken N.; Lander, Eric S.; Golub, Todd R. (January 2003). "A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors". Nature Genetics. 33 (1): 49–54. doi:10.1038/ng1060. ISSN 1546-1718. PMID 12469122. S2CID 12059602.
- ^ a b Napoli I, Mercaldo V, Boyl PP, Eleuteri B, Zalfa F, De Rubeis S, Di Marino D, Mohr E, Massimi M, Falconi M, Witke W, Costa-Mattioli M, Sonenberg N, Achsel T, Bagni C (September 2008). "The Fragile X Syndrome Protein Represses Activity-Dependent Translation through CYFIP1, a New 4E-BP". Cell. 134 (6): 1042–1054. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.031. PMID 18805096. S2CID 14123165.
- ^ Zalfa F, Giorgi M, Primerano B, Moro A, Di Penta A, Reis S, Oostra B, Bagni C (February 2003). "The fragile X syndrome protein FMRP associates with BC1 RNA and regulates the translation of specific mRNAs at synapses". Cell. 112 (3): 317–27. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00079-5. PMID 12581522. S2CID 14892764.
- ^ a b Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- ^ a b c Connolly E, Braunstein S, Formenti S, Schneider RJ (May 2006). "Hypoxia inhibits protein synthesis through a 4E-BP1 and elongation factor 2 kinase pathway controlled by mTOR and uncoupled in breast cancer cells". Mol. Cell. Biol. 26 (10): 3955–65. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.10.3955-3965.2006. PMC 1489005. PMID 16648488.
- ^ Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- ^ a b c Mader S, Lee H, Pause A, Sonenberg N (September 1995). "The translation initiation factor eIF-4E binds to a common motif shared by the translation factor eIF-4 gamma and the translational repressors 4E-binding proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (9): 4990–7. doi:10.1128/MCB.15.9.4990. PMC 230746. PMID 7651417.
- ^ Rao RD, Mladek AC, Lamont JD, Goble JM, Erlichman C, James CD, Sarkaria JN (October 2005). "Disruption of parallel and converging signaling pathways contributes to the synergistic antitumor effects of simultaneous mTOR and EGFR inhibition in GBM cells". Neoplasia. 7 (10): 921–9. doi:10.1593/neo.05361. PMC 1502028. PMID 16242075.
- ^ Eguchi S, Tokunaga C, Hidayat S, Oshiro N, Yoshino K, Kikkawa U, Yonezawa K (July 2006). "Different roles for the TOS and RAIP motifs of the translational regulator protein 4E-BP1 in the association with raptor and phosphorylation by mTOR in the regulation of cell size". Genes Cells. 11 (7): 757–66. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2006.00977.x. PMID 16824195. S2CID 30113895.
- ^ Yang D, Brunn GJ, Lawrence JC (June 1999). "Mutational analysis of sites in the translational regulator, PHAS-I, that are selectively phosphorylated by mTOR". FEBS Lett. 453 (3): 387–90. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00762-0. PMID 10405182. S2CID 5023204.
- ^ Patel J, McLeod LE, Vries RG, Flynn A, Wang X, Proud CG (June 2002). "Cellular stresses profoundly inhibit protein synthesis and modulate the states of phosphorylation of multiple translation factors". Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (12): 3076–85. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02992.x. PMID 12071973.
- ^ a b Kumar V, Sabatini D, Pandey P, Gingras AC, Majumder PK, Kumar M, Yuan ZM, Carmichael G, Weichselbaum R, Sonenberg N, Kufe D, Kharbanda S (April 2000). "Regulation of the rapamycin and FKBP-target 1/mammalian target of rapamycin and cap-dependent initiation of translation by the c-Abl protein-tyrosine kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (15): 10779–87. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.15.10779. PMID 10753870.
- ^ Kumar V, Pandey P, Sabatini D, Kumar M, Majumder PK, Bharti A, Carmichael G, Kufe D, Kharbanda S (March 2000). "Functional interaction between RAFT1/FRAP/mTOR and protein kinase cdelta in the regulation of cap-dependent initiation of translation". EMBO J. 19 (5): 1087–97. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.5.1087. PMC 305647. PMID 10698949.
- ^ Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Raught B, Polakiewicz RD, Abraham RT, Hoekstra MF, Aebersold R, Sonenberg N (June 1999). "Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: a novel two-step mechanism". Genes Dev. 13 (11): 1422–37. doi:10.1101/gad.13.11.1422. PMC 316780. PMID 10364159.
- ^ Shen X, Tomoo K, Uchiyama S, Kobayashi Y, Ishida T (October 2001). "Structural and thermodynamic behavior of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in supramolecular formation with 4E-binding protein 1 and mRNA cap analogue, studied by spectroscopic methods". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 49 (10): 1299–303. doi:10.1248/cpb.49.1299. PMID 11605658.
- ^ Adegoke OA, Chevalier S, Morais JA, Gougeon R, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS, Wing SS, Marliss EB (January 2009). "Fed-state clamp stimulates cellular mechanisms of muscle protein anabolism and modulates glucose disposal in normal men". Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 296 (1): E105–13. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90752.2008. PMC 2636991. PMID 18957614.
- ^ Pause A, Belsham GJ, Gingras AC, Donzé O, Lin TA, Lawrence JC, Sonenberg N (October 1994). "Insulin-dependent stimulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of a regulator of 5'-cap function". Nature. 371 (6500): 762–7. Bibcode:1994Natur.371..762P. doi:10.1038/371762a0. PMID 7935836. S2CID 4360955.
- ^ Kleijn M, Scheper GC, Wilson ML, Tee AR, Proud CG (December 2002). "Localisation and regulation of the eIF4E-binding protein 4E-BP3". FEBS Lett. 532 (3): 319–23. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03694-3. PMID 12482586. S2CID 24527449.
- ^ Poulin F, Gingras AC, Olsen H, Chevalier S, Sonenberg N (May 1998). "4E-BP3, a new member of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein family". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (22): 14002–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.22.14002. PMID 9593750.
- ^ Dostie J, Ferraiuolo M, Pause A, Adam SA, Sonenberg N (June 2000). "A novel shuttling protein, 4E-T, mediates the nuclear import of the mRNA 5' cap-binding protein, eIF4E". EMBO J. 19 (12): 3142–56. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.12.3142. PMC 203362. PMID 10856257.
- ^ Vary TC, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR (December 1999). "Amino acid-induced stimulation of translation initiation in rat skeletal muscle". Am. J. Physiol. 277 (6 Pt 1): E1077–86. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.1999.277.6.E1077. PMID 10600798.
- ^ Harris TE, Chi A, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Rhoads RE, Lawrence JC (April 2006). "mTOR-dependent stimulation of the association of eIF4G and eIF3 by insulin". EMBO J. 25 (8): 1659–68. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601047. PMC 1440840. PMID 16541103.
- ^ Gradi A, Imataka H, Svitkin YV, Rom E, Raught B, Morino S, Sonenberg N (January 1998). "A novel functional human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (1): 334–42. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.1.334. PMC 121501. PMID 9418880.
추가 정보
- Jain S, Khuri FR, Shin DM (2004). "Prevention of head and neck cancer: current status and future prospects". Current Problems in Cancer. 28 (5): 265–86. doi:10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2004.05.003. PMID 15375804.
- Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Borden KL (2007). "Controlling gene expression through RNA regulons: the role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E". Cell Cycle. 6 (1): 65–9. doi:10.4161/cc.6.1.3688. PMID 17245113.
- Malys N, McCarthy JE (2010). "Translation initiation: variations in the mechanism can be anticipated". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 68 (6): 991–1003. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0588-z. PMID 21076851. S2CID 31720000.
외부 링크
- Nature Reviews Microbiology로부터의 상한 의존 번역 개시.개시 요인의 기능에 대한 양호한 이미지와 개요.