미토콘드리아 리보솜 단백질 L22
Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L22| MRPL22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 식별자 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 에일리어스 | MRPL22, L22mt, MRP-L22, MRP-L25, RPML25, HSPC158, 미토콘드리아 리보솜 단백질 L22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 외부 ID | OMIM : 611835 MGI : 1333794 HomoloGene : 56664 GenCard : MRPL22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 위키데이터 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
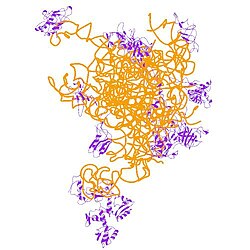
39S 리보솜 단백질 L22, 미토콘드리아는 사람에게서 MRPL22 [5]유전자에 의해 암호화되는 단백질이다.
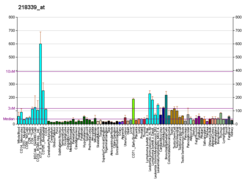
포유류의 미토콘드리아 리보솜 단백질은 핵 유전자에 의해 암호화되어 미토콘드리아 내 단백질 합성에 도움을 준다.미토콘드리아 리보솜(미토콘드리아 리보솜)은 작은 28S 서브유닛과 큰 39S 서브유닛으로 구성된다.그들은 원핵생물 리보솜에 비해 단백질 대 rRNA 조성이 75%로 추정되며, 이 비율은 역전된다.포유류의 미토리보솜과 원핵생물 리보솜의 또 다른 차이점은 5S rRNA를 포함하고 있다는 것이다.종별로 미토리보솜을 구성하는 단백질의 배열이 크게 다르며 때로는 생화학적 성질이 다르므로 시퀀스 호몰로지로 쉽게 인식할 수 없다.이 유전자는 L22 리보솜 단백질군에 속하는 39S 서브유닛 단백질을 암호화합니다.이 유전자에 대응하는 의사유전자가 염색체 4q에서 발견된다.이 [5]유전자에 대해 서로 다른 아이소폼을 코드하는 두 개의 전사 변형이 발견되었다.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG000082515 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000020514 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MRPL22 mitochondrial ribosomal protein L22".
추가 정보
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Goldschmidt-Reisin S, Kitakawa M, Herfurth E, et al. (1999). "Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal proteins. N-terminal amino acid sequencing, characterization, and identification of corresponding gene sequences". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (52): 34828–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.52.34828. PMID 9857009.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Kenmochi N, Suzuki T, Uechi T, et al. (2001). "The human mitochondrial ribosomal protein genes: mapping of 54 genes to the chromosomes and implications for human disorders". Genomics. 77 (1–2): 65–70. doi:10.1006/geno.2001.6622. PMID 11543634.
- Koc EC, Burkhart W, Blackburn K, et al. (2001). "The large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome. Analysis of the complement of ribosomal proteins present". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (47): 43958–69. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106510200. PMID 11551941.
- O'Brien TW (2002). "Evolution of a protein-rich mitochondrial ribosome: implications for human genetic disease". Gene. 286 (1): 73–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00808-3. PMID 11943462.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Zhang Z, Gerstein M (2003). "Identification and characterization of over 100 mitochondrial ribosomal protein pseudogenes in the human genome". Genomics. 81 (5): 468–80. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00004-1. PMID 12706105.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.