비트
NORBIT전자제품에서 NORB는모듈 IT 패밀리는 Philips가 개발한 디지털 로직의 초기 형태(1960년 이후[1][2][3][4][5]로[6][7], 개별 컴포넌트를 포함한 모듈을 사용하여 저항 트랜지스터 로직(RTL)[8][4] 또는 다이오드 트랜지스터 로직(DTL) 테크놀로지로 논리 기능 블록을 구축합니다.
개요
시스템은 원래 solid-state[3][5]하드웨어에 내장된 프로그래밍 논리 제어 장치에 건물 블록(프로그램 가능 논리 제어기의 전임자들(PLC))로 공정 제어와 자동화 응용 프로그램 초기 Telefunken/AEG Logistat 지멘스는 심과 비슷한 산업용 제어 시스템에서 전기 기계 릴레이 논리를 대체하기 위하여 고안되었다.atic,BBC Sigmatronic, ACEC Logacec 또는 Akord Estacord 시스템.[3][9][10][11][12]
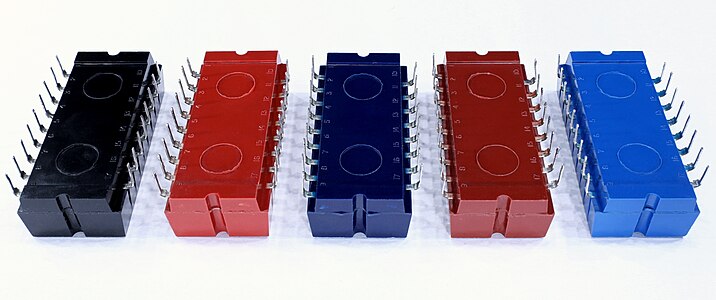
사용 가능한 각 논리 함수는 플라스틱 용기 색상(검은색, 파란색, 빨간색, 녹색, 보라색 등)으로 식별할 수 있었습니다.가장 중요한 회로 블록에는 NOR 게이트(이름을 따옴)가 포함되어 있었지만 드라이버를 포함한 블록과 최신 555 타이머 [8][13][14]IC와 유사한 타이머 회로도 있었습니다.
1960년에 도입된 YL 6000 시리즈의 오리지널 Norbit 모듈에는 최대 10개의 긴 비행 리드가 [4][5][15]연속해서 최대 5개의 리드로 구성된 2개의 그룹으로 배열된 단일 인라인 패키지가 포함되어 있습니다.이 모듈은 ±24V [4][15]공급기에서 1kHz 미만의 주파수에 대해 지정되었습니다.
1960년에는 PCB에 [1][16][17][18][13][15]장착하기 위해 10개의 균일한 간격의 견고한 리드를 가진 싱글인 라인 패키지로 Combi-Element[2][1][3][13][nb 1] 모듈도 제공되었습니다(5.08mm/0.2인치 피치).이들은 ±6V의 전원을 [1][15]가진 1시리즈(일명 "100kHz 시리즈")[13][nb 2]로 그룹화되었습니다.새로운 10시리즈와 20시리즈의 패키지는 크기가 비슷했지만, 총 19개의 [18][13]리드선을 위해 9개의 리드선을 병렬로 추가했습니다.10시리즈는 게르마늄 합금 트랜지스터를 사용하는 반면, 20시리즈의 실리콘 평면 트랜지스터는 최대 1MHz(대 30kHz)의 높은 컷오프 주파수 및 +85°C(대 +55°[18]C)의 높은 허용 온도 범위에 사용됩니다.
1967년 필립스/멀러드 NORB는IT2[19][20][21] Valvo NORBIT-S[22][23][24][nb 3] 모듈 패밀리가 도입되었습니다.처음에는 24V의 [19]단일 공급 전압으로 최대 10kHz의 주파수를 지원하는 60시리즈로[25] 구성되어 있습니다.나중에 사이리스터 트리거 및 제어 모듈을 포함하는 61 [19]시리즈가 추가되었습니다.90시리즈는[26][nb 4] 1970년대 중반에도 사용할 수 있게 되었습니다.대형(1x2인치) 17핀 듀얼 인라인 패키지에 포함된 기본적인 타입은 3종류입니다.한쪽은 5.08mm(0.2인치) 간격으로 9핀, 반대쪽은 [27][28]8핀으로 되어 있습니다.
모듈
오리지널 Norbit 패밀리
- YL 6000 시리즈
- YL6000 - NOR 게이트(빨간색)("NOR")[4][15]
- YL6001 - 이미터 팔로어(노란색) ('EF')[4][15]
- YL6004 - 고출력 (더블 사이즈 모듈) ('HP')[4][15]
- YL6005, YL6005/00 - 카운터 유닛 (트리플 바이너리) ("3C")[4][15] (보라색)
- YL6005/05 - 싱글 나눗셈 by 2 카운터 (바이올렛) ('1C')[4]
- YL6006 - 타이머 (갈색) ('TU')[4][15]
- YL6007 - 섀시 ('CU')[4][15]
- YL6008 - 중간 출력 (주황색) ('MP')[4][15]
- YL6009 - 저전력 출력 (흰색) ('LP')[4][15]
- YL6010 - 광전 검출기 헤드("PD")[4][15]
- YL6011 - 광전 램프 헤드("PL")[4][15]
- YL6012 - 트윈 2입력 NOR 게이트 (검은색) ('2.2 NOR')[4][15]
- YL 6100 시리즈
- YL6101 - 정류기[15] 유닛
- YL6102 - 정류기 유닛[15]
- YL6103/00 - Regel-Einheit[15]
- YL6103/01 - Regel-Einheit[15]
- YL6104 - Léngsglied für Regel-Einheit[15]
- YL6105 - Regel-Einheit[15]
- 릴레이 시리즈
- 88930/30 - Eingangs-/Ausgangseinheit[15]
- 88930/33 - Vorwahl-Zéhleinheit[15]
- 88930/36 - Zweifach-Programm-Einheit[15]
- 88930/37 - Vierfach-Programm-Einheit[15]
- 88930/39 - Ausgangs-Einheit[15]
- 88930/42 - Leer-Einheit[15]
- 88930/48 - 임펄스[15] 전-아인하이트
- 88930/51 - Programmed-Vorbereitungs-Einheit[15]
- 88930/54 - Rückstell-Einheit[15]
- 88930/57 - Relais-Verstarker-Einheit[15]
- 88930/60 - Relaisblock-Einheit[15]
- 88930/64 - Spise-Einheit[15]
콤비 엘리먼트 패밀리
- 1 시리즈 / B8900 시리즈
- B893000, B164903 - 트윈 3입력 AND 게이트 (오렌지색) ("2.3A1", "2x3N1")[1][15]
- B893001, B164904 - 트윈 2입력 AND 게이트 (오렌지색) ('2.2A1', '2x2N1')[1][15]
- B893002, 2P72729 - 트윈 3입력 OR 게이트(오렌지색) ('2.3O1', '23O1', '2x3P1')[1][29][15]
- B893003, 2P72730 - 트윈 2입력 OR 게이트(오렌지색) ('2.2O1', '22O1', '2x2P1')[1][15]
- B894002, B164910 - 트윈 인버터 앰프(노란색)("2IA1", "2")IA1", "2xIA1"[1][13])[15]
- B894005, 2P72728 - 트윈 인버터 앰프(노란색)("2IA2", "2xIA2")[1][15]
- B894001, B164909 - 트윈 이미터 팔로어 (노란색) ("2EF1", 2xEF1")[1][15]
- B894003, 2P72727 - 트윈 이미터 팔로어(노란색) ('2EF2', '2xEF2')[1][15]
- B894000, B164907 - 이미터 팔로어/인버터 앰프(노란색)("EF1/IA1")[1][15]
- B895000, B164901 - 펄스 셰이퍼(슈미트 트리거 + 앰프)(녹색)('PS1')[1][15]
- B895001, B164908 - 원샷 멀티바이저 ('OS1')[1][15]
- B895003 - 원샷 멀티바이저 ('OS2')[15]
- B892000, B164902 - 플립 플랍 (빨간색) ('FF1')[1][15]
- B892001, 2P72707 - 시프트 레지스터 플립 플랍 (빨간색) ('FF2')[1][29][15]
- B892002 - 플립 플랍 (빨간색) ('FF3')[29][15][18]
- B892003 - 플립 플랍 (빨간색) ('FF4')[15]
- B893004, 2P72726 - 펄스 로직 (주황색) ('PL1', '2xPL1')[1][15]
- B893007 - 펄스 로직 (오렌지색) ('2xPL2')[15]
- B885000, B164911 - Decade 카운터("[1][15]DC1")
- B8900 - 파워앰프('PA1')[15]
- B896000 - 코어 메모리용 트윈 셀렉터 스위치("2SS1")[1]
- B893005 - 코어 메모리용 선택 게이트("SG1")[1]
- 2P72732 - 코어 메모리용 펄스 발생기("PG1")[1]
- 2P72731 - 코어 메모리용 읽기 증폭기("RA1")[1]
- 10 시리즈
- 2P73701 - 플립 플랍 ('FF10')[18][30]
- 2P73702 - 플립 플랍 ('FF11')[18][30]
- 2P73703 - 플립 플랍 / 쌍안정 멀티 바이브레이터(트리거 게이트 내장) 및 설정 리셋 입력(검은색)("FF12")[13][30]
- 듀얼 트리거 게이트("2")TG13 인치)[18][30]
- 듀얼 트리거 게이트("2")TG14 인치)[18][30]
- 쿼드러플 트리거 게이트("4")TG15 인치)[18][30]
- 이중 양극 게이트 인버터 앰프("2")GI10")[18][30]
- 이중 양극 게이트 인버터 앰프("2")GI11 [18][30]인치)
- 이중 양극 게이트 인버터 앰프("2")GI12 인치)[18][30]
- 게이트 앰프("GA11")[18][30]
- 원샷 멀티바이저('OS11')[18][30]
- 타이머 유닛('TU10')[18][30]
- 펄스 드라이버('PD11'[18][30]
- 릴레이 드라이버('RD10')[18][30]
- 릴레이 드라이버('RD11')[30]
- 파워앰프('PA10')[18][30]
- 펄스 셰이퍼("PS10")[18][30]
- 숫자 표시 튜브 드라이버("ID10")[30]
- 20 시리즈
- 2P73710 - (2).GI12", "2GI12")[18]
Norbit 2 / Norbit-S 패밀리
- 60 시리즈
- 2NOR60, 2NOR60 - 트윈 NOR(검은색)[19][13][30]
- 4NOR60, 4NOR60 - 4중 NOR(검은색)[19][13][30]
- 2.IA60, 2IA60 - 저출력용 트윈 인버터 앰프(파란색)[19][13][30]
- LPA60 - 트윈 저전력[13] 출력
- 2. LPA60, 2LPA60 - 트윈 저전력 출력(파란색)[19][30]
- PA60 - 중간 출력(파란색)[19][13][30]
- HPA60 - 고출력(검은색)[19][13]
- 2. SF60, 2SF60 - 트윈 입력 스위치 필터(녹색)[19][13][30]
- TU60 - 타이머(빨간색)[19][13][30]
- FF60 - 플립 플랍[13]
- GLD60 - 접지된 로드 드라이버(검은색)[19][13]
- 61 시리즈
- TT61 - 트리거 변압기[19][30]
- 아시아 출장 매춘부가 그녀의 피부가 두꺼워진 클라이언트이다.
- RSA61 - 정류기 및 싱크로나이저[19][30]
- DOA61 - 디퍼렌셜 OP[19][30] 앰프
- 2NOR61, 2.NOR61 - 트윈[19][13][30] NOR
- 90 시리즈
- 악세사리
사진 갤러리
- 60 시리즈 NORB의 예IT2 패밀리
- 60 시리즈 NORB를 사용하는 프린트 회로 기판의 예IT2 패밀리
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
메모들
- ^ Mullard는 이 모듈을 영국에서 Combi-Element라고 불렀고 Philips와 Valvo는 회로 블록이라고 불렀지만 원래의 Norbit 시리즈와는 구별했습니다.
- ^ 이후 일부 데이터 시트는 100kHz 시리즈와 1-시리즈를 구분합니다.
- ^ 지금까지 Valvo [de의 Norbit-S 시리즈와 Philips Norbit 2 시리즈의 등가성은 1967년 출시일을 기준으로 합니다.종종, 새로운 패밀리의 모듈은 여전히 Norbits로만 언급되었습니다.
- ^ 90 시리즈의 모듈은 초기 데이터 시트에서 60 시리즈로 그룹화되었습니다.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Guide to Circuit Blocks (Combi-Elements) and their use in Digital Systems and Equipment - Part IV" (PDF). Sub-Assemblies Bulletin. Manor Royal Crawley, Sussex, England: Mullard Equipment Limited (9). November 1962 [May 1960]. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-20. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ a b "Prefabricated Electronic Bricks" (PDF). Wireless World. Technical Notebook. 66 (8): 374. August 1960. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
[…] ready-assembled circuit modules can cut down development time spent on a control-engineering or data processing problem by eliminating the work of designing individual circuits. A particular range made by Mullard are slim colour-coded plastics "boxes" of guaranteed performance specifications covering the commonly used circuit functions. Typical units are AND/OR gates, timing and relay-operating circuits called "Norbits" (for control purposes) and flip-flop, pulse shaper and inverter-amplifier stages called Combi elements (for digital circuits). By giving only a performance specification the manufacturers can take advantage of advances in techniques (for instance, complete solid-state circuits) without, at the same time, rendering obsolete existing apparatus. Transistors are used throughout, so that battery operation is reasonably economical, and the modules are designed to connect together compatibly in a manner suited to their functions. Norbits have long, flexible flying leads for use with terminal blocks while Combi-elements have short, stiff tinned wires suitable for fitting into printed wiring boards. […]
- ^ a b c d "INTERKAMA 1960 - Dusseldorf Exhibition of Automation and Instruments" (PDF). Wireless World. 66 (12): 588–589. December 1960. Retrieved 2018-06-18.
[…] Another point noticed was the widespread use of small-package solid-state logic (such as "and," "or," "not") and instrumentation (timers, amplifiers, etc.) units. There would seem to be a good case here for the various manufacturers to standardise practical details such as mounting, connections and power supplies so that a Siemens "Simatic," say, is directly interchangeable with an Ateliers des Constructions Electronique de Charleroi "Logacec," a Telefunken "Logistat," or a Mullard "Norbit" or "Combi-element." […]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Norbit Sub-Assemblies YL 6000 Series (PDF). Norbit Handbook (2 ed.). Mullard Equipment Limited. February 1962. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-20. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ a b c "les relais statiques Norbit". Revue MBLE (in French). Brussels, Belgium: Philips Research Laboratory, Manufacture Belge de Lampes et de Materiel Electronique (MBLE Research Laboratory). September 1962. Archived from the original on 2018-06-18. Retrieved 2018-06-18. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7]
- ^ "Judicial Greffe - Trademarks Database - Individual Record - NORBITS - TM 2671 - Mullard Limited". 2003-03-26 [1967-06-27]. Archived from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
- ^ "Judicial Greffe - Trademarks Database - Individual Record - NORBIT - TM 2672 - Mullard Limited". 2003-03-26 [1967-06-27]. Archived from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
- ^ a b Pistorius, Arthur (September 2007). "Retronics - Philips 60-series NORbits (1968)". Elektor Electronics. 2007 (9): 76. Retrieved 2018-06-20. [8]
- ^ Estacord - Das universelle Bausteinsystem für kontaktlose Steuerungen (Catalog) (in German). Herxheim/Pfalz, Germany: Akkord-Radio GmbH.
- ^ Klingelnberg, W. Ferdinand (2013) [1967, 1960, 1939]. Pohl, Fritz; Reindl, Rudolf (eds.). Technisches Hilfsbuch (in German) (softcover reprint of 15th hardcover ed.). Springer-Verlag. p. 135. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-88367-5. ISBN 978-3-64288368-2. LCCN 67-23459. 0512.
- ^ Weißel, Ralph; Schubert, Franz (2013-03-07) [1995, 1990]. "4.1. Grundschaltungen mit Bipolar- und Feldeffekttransistoren". Digitale Schaltungstechnik. Springer-Lehrbuch (in German) (reprint of 2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag. p. 116. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-78387-6. ISBN 978-3-540-57012-7.
- ^ Walker, Mark John (2012-09-08). The Programmable Logic Controller: its prehistory, emergence and application (PDF) (PhD thesis). Department of Communication and Systems Faculty of Mathematics, Computing and Technology: The Open University. pp. 223, 269, 308. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-20. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Wylie, Andrew (2009). "Packaged circuits". Archived from the original on 2018-06-18. Retrieved 2019-06-22.
- ^ "Schakelen met de 60-serie NORBITs" (in Dutch). Philips. (NB. Green cover.)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba Valvo-Taschenbuch (in German) (1964 ed.). Hamburg, Germany: Valvo GmbH. 1964. [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] (NB. An English version of this book was also available as Valvo Pocketbook.)
- ^ Mullard Combi Elements (PDF). Mullard. 1963 [May 1960]. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-20. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ Gossel, Dieter; Kaps, Gerhard; Schott, Winfried (1965). "A new system of digital circuit blocks for industrial measuring and control equipment" (PDF). Philips Technical Review. Philips Zentrallaboratorium GmbH, Hamburg, Germany: Philips. 26 (4/5/6): 164–170. 621.374.32. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t van Barneveld, Evert Jan (1967). "Digital circuit blocks" (PDF). Philips Technical Review. Philips Electronic Components and Materials Product Division (Elcoma), Eindhoven, Netherlands: Philips. 28 (2): 44–56. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y NORBIT 2 and 61 SERIES - Solid state control elements - Data sheets. Mullard Limited. March 1974. TP1428. [14] [15] [16] [17] [18]
- ^ Philips Nederland n.v. (June 1967). "Kijk: Norbit 2 is er! Statisch schakelen is nu óók goedkoop schakelen" (PDF). Elektuur (Advertisement) (in Dutch). Eindhoven, Netherlands (54): 604.
- ^ NORBIT 2 - Low Priced Static Switches. Philips. 1967.
- ^ Norbit-S-Kompendium (in German). Hamburg, Germany: Valvo GmbH / Curtze. April 1969. (128 pages + appendix)
- ^ Dokter, Folkert; Steinhauer, Jürgen (1973-06-18). "6.5. Digital modules with discrete components". Digital Electronics. Philips Technical Library (PTL) / Macmillan Education (Reprint of 1st English ed.). Eindhoven, Netherlands: The Macmillan Press Ltd. / N. V. Philips' Gloeilampenfabrieken. pp. 226, 232. doi:10.1007/978-1-349-01417-0. ISBN 978-1-349-01419-4. SBN 333-13360-9. Retrieved 2018-07-01. (270 pages) (NB. This is based on a translation of volume I of the two-volume German edition.)
- ^ Dokter, Folkert; Steinhauer, Jürgen (1975) [1969]. "6.5.2 Bauformen digitaler Funktionsbausteine". Digitale Elektronik in der Meßtechnik und Datenverarbeitung: Theoretische Grundlagen und Schaltungstechnik. Philips Fachbücher (in German). Vol. I (improved and extended 5th ed.). Hamburg, Germany: Deutsche Philips GmbH. pp. 281–285. ISBN 3-87145-272-6. (xii+327+3 pages) (NB. The German edition of volume I was published in 1969, 1971, two editions in 1972, and 1975. Volume II was published in 1970, 1972, 1973, and 1975.)
- ^ Rosielle, C. (May 1968). Deerson, Jonathan (ed.). Control system design manual for 60-series NORbits: A Guide to the application of electronic logic circuits in industry. Philips Application Book (1 ed.). Eindhoven, Netherlands: N.V. Philips' Gloeilampenfabrieken, Electronic Components and Materials Division (Elcoma), Technical Publications Department. 9399 263 016 01. [19] (233+8 pages) (NB. There exists a fourth edition from 1974 as well.)
- ^ Semiconductors - Part 5 - Field-effect transistors (PDF). Electronic components and materials (Elcoma) - Philips Data Handbook. Philips. October 1980. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
[…] COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS (GREEN SERIES) […] Part 1 - July 1979 - CM107-79 - Assemblies for industrial use PLC modules, high noise immunity logic FZ/30 series, NORbits 60-series, 61-series, 90-series, input devices, hybrid integrated circuits, peripheral devices […]
- ^ Schakelen met NORBITs (in Dutch). Philips. (NB. 갈색 커버).
- ^ Dean, K. J. (January–February 1973). "Trends in semiconductor digital circuits". Radio and Electronic Engineer. IET. 43 (1.2): 67–74. doi:10.1049/ree.1973.0011. ISSN 0033-7722. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ a b c Reuvers, Paul; Simons, Marc (2018-02-24) [2017-11-28]. "Circuit Blocks". www.cryptomuseum.com. Archived from the original on 2018-06-18. Retrieved 2018-06-17.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag Components and materials - Part 1: Circuit blocks, Input/Output devices (PDF). Philips Data Handbook. Philips. September 1970. 9399 261 14901. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-20. Retrieved 2018-06-20. (NB. 녹색 커버가 있습니다.)
추가 정보
- Norbit-Bausteine (in German). Valvo GmbH. 1962. (43페이지) (NB. Valvo-Handbucch 1962 페이지 83~125의 일부이기도 합니다.)
- Valvo-Handbuch Bausteine (in German) (1963 ed.). Hamburg, Germany: Valvo GmbH. 1963. (253 페이지) (NB. Norbit 모듈에 대한 장도 포함되어 있습니다.)
- Norbit-S-Bausteine (in German) (1967/1968 ed.). Hamburg, Germany: Valvo GmbH. 1967. (25페이지)
- Circuit Blocks 40-Series, NORBITS 60-Series, Input/Output Devices. Philips Product Data. Philips Electronic Components and Materials Division. September 1969. 9399 261 10501. [20]
- Grimley, Robert (2016) [2011]. "Mullard & CES - Mullard & Combined Electronic Services (CES)". Early Philips Colour TV. Archived from the original on 2017-10-27. Retrieved 2017-01-14.
외부 링크
- Holm, Åke. "Picture of four NORBIT 2 modules". Archived from the original on 2018-06-19. Retrieved 2018-06-19.