하이퍼림플렉스
Hypersimplex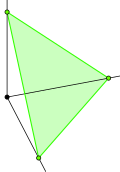 | 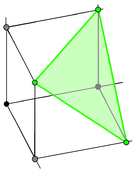 |
하이퍼플레인: + + = 1 } | 하이퍼플레인: + + = 2 } |
|---|
다면 결합체학에서 초심플렉스 , 는 심플렉스를 일반화하는 볼록 폴리토프다.두 정수 {\d}k {\에 의해 결정되며, k k와 d- k 0으로 구성된 차원 벡터의 볼록 선체로 정의된다.동등하게 , d{ d을 + + = k ={\{d}}}}}}}}}}}d}}}}d}d}d}d}d}d}d}d}을 자르면 얻을 수 있다. 및 이러한 로0 < < d< d < ( -차원 폴리토프 입니다[1]
특성.
The number of vertices of is .[1] The graph formed by the vertices and edges of the hypersimplex is the Johnson graph .[2]
대체 구성
대안적 구조( / 의 경우는 - 1 또는 0 좌표가 있는 모든(- k- 벡터의 볼록 선체를 취한다.이는 결과적인 폴리토페와 같은 차원인 공간에서 운용할 수 있다는 장점이 있지만, 결과적인 폴리토페가 만들어내는 단점은 덜 대칭적이다(다른 구성의 결과와 조합적으로 동일하지만).
초대칭 , 는 d{\ 요소와 k{\가 있는 균일한 매트로이드의 매트로이드 폴리토프이기도 하다[3]
예
초대칭 , 1 }은 a( d- ){\-simplex( d{\정점)이다.초대형 , 은 옥타헤드론이고, 초대형 , 5,은 정류형 5셀이다.
Generally, the hypersimplex, , corresponds to a uniform polytope, being the -rectified -dimensional simplex, with vertices positioned at the center of all the -dimensional faces of a - ) -차원 심플렉스.
| 이름 | 등각형 삼각형의 | 사면체 (3-630x) | 팔면체 | 5세포 (4-980x) | 수정됨 5세포 | 5와섹스 | 수정됨 5와섹스 | 양방향으로 5와섹스 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δd,k = (d,k) = (d,d -k) | (3,1) (3,2) | (4,1) (4,3) | (4,2) | (5,1) (5,4) | (5,2) (5,3) | (6,1) (6,5) | (6,2) (6,4) | (6,3) |
| 정점 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 15 | 20 |
| d-message | (0,0,1) (0,1,1) | (0,0,0,1) (0,1,1,1) | (0,0,1,1) | (0,0,0,0,1) (0,1,1,1,1) | (0,0,0,1,1) (0,0,1,1,1) | (0,0,0,0,0,1) (0,1,1,1,1,1) | (0,0,0,0,1,1) (0,0,1,1,1,1) | (0,0,0,1,1,1) |
| 이미지 |  |  |  | 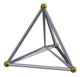 |  | |||
| 그래프 |  J(3,1) = K2 |  J(4,1) = K3 | 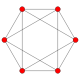 J(4,2) = T(6,3) | 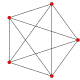 J(5,1) = K4 | 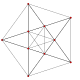 J(5,2) |  J(6,1) = K5 | 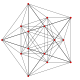 J(6,2) |  J(6,3) |
| 콕시터 도표 | ||||||||
| 슐레플리 기호 | {3} = r{3} | {3,3} = 2r{3,3} | r{3,3} = {3,4} | {3,3,3} = 3r{3,3} | r{3,3,3} = 2r{3,3} | {3,3,3,3} = 4r{3,3,3} | r{3,3,3} = 3r{3,3,3} | 2r{3,3,3} |
| 면 | { } | {3} | {3,3} | {3,3}, {3,4} | {3,3,3} | {3,3,3}, r{3,3,3} | r{3,3,3} | |
역사
초임플레스는 가브리엘로프, 젤리팬드 & 로식(1975년)에 의해 특성 클래스(대수학적 위상에서의 중요한 주제)의 계산에서 먼저 연구되고 명명되었다.[4][5]
참조
- ^ a b Miller, Ezra; Reiner, Victor; Sturmfels, Bernd, Geometric Combinatorics, IAS/Park City mathematics series, vol. 13, American Mathematical Society, p. 655, ISBN 9780821886953.
- ^ Rispoli, Fred J. (2008), The graph of the hypersimplex, arXiv:0811.2981, Bibcode:2008arXiv0811.2981R.
- ^ 특히 114페이지의 8.20항에 따른 발언을 참조하십시오Grötschel, Martin (2004), "Cardinality homogeneous set systems, cycles in matroids, and associated polytopes", The Sharpest Cut: The Impact of Manfred Padberg and His Work, MPS/SIAM Ser. Optim., SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 99–120, MR 2077557.
- ^ Gabrièlov, A. M.; Gelʹfand, I. M.; Losik, M. V. (1975), "Combinatorial computation of characteristic classes. I, II", Akademija Nauk SSSR, 9 (2): 12–28, ibid. 9 (1975), no. 3, 5–26, MR 0410758.
- ^ Ziegler, Günter M. (1995), Lectures on Polytopes, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, vol. 152, Springer-Verlag, New York, p. 20, doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-8431-1, ISBN 0-387-94365-X, MR 1311028.
추가 읽기
- Hibi, Takayuki; Solus, Liam (2016), "Facets of the r-stable (n,k)-hypersimplex", Annals of Combinatorics, 20: 815–829, arXiv:1408.5932, Bibcode:2014arXiv1408.5932H, doi:10.1007/s00026-016-0325-x.


 심플렉스를 일반화하는
심플렉스를 일반화하는 


![[0,1]^{d}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e13ae4917276744b214714a20b3cb8ee305e309d)










 .
. 


