시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스
Cytochrome b6f complex| 시토크롬 b6f 복합체 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| 식별자 | |||||||||
| 기호 | B6F | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF05115 | ||||||||
| 인터프로 | IPR007802 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 3.D.3 | ||||||||
| OPM 슈퍼 패밀리 | 92 | ||||||||
| OPM단백질 | 4평1길 | ||||||||
| 멤브라노메 | 258 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| 시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 식별자 | |||||||||
| EC 번호 | 1.10.99.1 | ||||||||
| 데이터베이스 | |||||||||
| 인텐츠 | IntEnz 뷰 | ||||||||
| 브렌다 | 브렌다 입력 | ||||||||
| 엑스퍼시 | 나이스자이메 뷰 | ||||||||
| 케그 | KEG 입력 | ||||||||
| 메타사이크 | 대사통로 | ||||||||
| 프리암 | 프로필 | ||||||||
| PDB 구조 | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
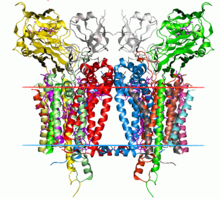
시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스(plastokinol—plastocyanin reducationase; EC 1.10.99.1)는 식물, 시아노박테리아, 녹조의 엽록체 내 태라코이드 막에서 발견되는 효소로, 플라토키놀에서 플라스토시아닌으로의 전자의 전달을 촉진한다.[1]이 반응은 미토콘드리아 전자 전송 체인의 시토크롬 bc1(Complex III)에 의해 촉매된 반응과 유사하다.광합성 과정에서 시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스는 포토시스템 II에서 포토시스템 I로 전자를 전송하는 체인을 따라 한 단계 나아가는 동시에 양자를 태일라코이드 공간으로 펌핑하여 나중에 ADP로부터 ATP를 합성하는 데 사용되는 전기화학(에너지) 경사로의[2] 생성에 기여한다.
효소구조
시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스는 조광기로, 각 모노머는 8개의 서브유닛으로 구성되어 있다.[3]These consist of four large subunits: a 32 kDa cytochrome f with a c-type cytochrome, a 25 kDa cytochrome b6 with a low- and high-potential heme group, a 19 kDa Rieske iron-sulfur protein containing a [2Fe-2S] cluster, and a 17 kDa subunit IV; along with four small subunits (3-4 kDa):PetG, PetL, PetM, PetN.[3][4]총 분자량은 217 kDa이다.
클라미도모나스 라인하르디, 마스티고클라두스 라미노수스, 노스토크 sp의 시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스의 결정 구조.PCC 7120이 결정되었다.[2][5][6][7][8][9]null
이 단지의 핵심은 구조적으로 시토크롬 bc1 핵심과 유사하다.시토크롬 b와6 서브유닛 IV는 시토크롬 b와 동질이고,[10] 두 단지의 리스케 철황 단백질은 동질성이다.[11]그러나 시토크롬 f와 시토크롬 c는1 동음이의어가 아니다.[12]null
시토크롬 bf는6 7개의 보철물 그룹을 포함하고 있다.[13][14]시토크롬 bf와6 bc1 모두에서 4개가 발견되는데, 시토크롬 c와1 f의 c형 heme, bc와1 bf의6 b형 hemes(b와p bn), 리스케 단백질의 [2Fe-2S] 군집이다.시토크롬 bf에서는6 엽록소 a, β-카로틴, 헤메n c(Heme x라고도 한다)의 세 가지 독특한 보형물 그룹이 발견된다.[5]null
사이토크롬 b6f 콤플렉스 다이머의 코어 내 단층체간 공간은 지질들이 점유하고 있어 단백질 내 유전체 환경의 변조를 통해 헤메-헤메 전자 전달의 방향성을 제공한다.[9][15]null
생물 함수

광합성에서 시토크롬 bf6 복합체는 두 광합성 반응센터 복합체인 포토시스템 II와 포토시스템 I 사이에서 전자와 에너지의 전달을 중재하는 동시에 엽록체 스트롬으로부터 양성자를 태라코이드 막을 가로질러 루멘으로 전달한다.[2]사이토크롬 bf를6 통한 전자 운송은 엽록체에서 ATP의 합성을 추진하는 양성자 구배를 만드는 역할을 한다.[4]null
별도의 반응에서 시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스는 NADP가+ 감소된 페레독신으로부터 전자를 받아들일 수 없을 때 순환 광인산화의 중심 역할을 한다.[1]P700의+ 에너지에 의해 구동되는 이 사이클은 ATP 합성을 구동하는 데 사용할 수 있는 양성자 구배 생성에 기여한다.이 주기는 광합성에 필수적인 것으로 나타나 탄소 고정을 위한 ATP/NADPH 생산의 적정 비율을 유지하는 데 도움을 주고 있다.[16][17][18]null
시토크롬 b6f 콤플렉스 내의 p-side 퀴놀 디프로토네이션-산소화 반응은 활성산소 종의 생성에 관여했다.[19]키놀 산화 부위에 위치한 일체형 엽록소 분자는 반응성 산소 종의 형성 속도를 향상시키는 구조적인 비포토화학 기능을 수행하도록 제안되었으며, 이는 세포 내 통신을 위한 리독스 경로를 제공할 가능성이 있다.[20]null
반응 메커니즘
시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스는 두 모바일 레독스 캐리어인 플라스티누키놀(QH2)과 플라스토시아닌(Pc):
| H2O | → | 포토시스템 II | → | QH2 | → | Cyt b6f | → | pc | → | 포토시스템 I | → | NADPH | (1) |
| QH2 | → | Cyt b6f | → | pc | → | 포토시스템 I | → | Q | (2) | ||||
시토크롬 bf는6 플라스티누키놀에서 플라스토시아닌으로 전자의 전달을 촉진하는 동시에 스트로마에서 틸라코이드 루멘으로 두 개의 양성자를 펌프질한다.
- QH2 + 2Pc(Cu2+) + 2H+(스트로마) → Q + 2Pc(Cu+) + 4H+(루멘)[1]
이 반응은 콤플렉스 III에서와 같이 Q 사이클을 통해 발생한다.[21]플라토키놀은 전자 운반체 역할을 하며 전자 분기라는 메커니즘을 통해 두 개의 전자를 고전위 및 저전위 전자 전송 체인(ETC)에 전달한다.[22]이 복합체에는 Q 사이클의 작동과 광합성에서의 리독스 감지 및 촉매 기능을 담당하는 전자전달망을 형성하는 최대 3개의 플라토키논 분자가 들어 있다.[23]null
Q 사이클
Q 사이클 전반기
- QH는2 단지의 플러스 'p' 측(루멘 측)에 결합한다.철-황반(고전위 ETC)에 의해 세미키논(SQ)으로 산화되며, 두 개의 양성자를 태일라코이드 루멘에[citation needed] 방출한다.
- 환원된 철황중추는 사이토크롬 f를 통해 pc로 전자를 전달한다.
- 저전위 ETC에서 SQ는 전자를 사이토크롬 b6의 헴 b에p 전달한다.
- 헤메 b는p 그 다음에 전자를 헤메 b로n 옮긴다.
- 헤메 b는n 하나의 전자로 Q를 줄여 SQ를 형성한다.
Q 사이클 후반부
- 두번째 QH는2 단지와 결합한다.
- 고전위 ETC에서는 전자 하나가 또 다른 산화 pc를 감소시킨다.
- 저전위 ETC에서는 heme b에서n 나온 전자가 SQ로 전달되며, 완전히 줄어든2− Q는 스트로마에서 두 개의 양성자를 차지하여2 QH를 형성한다.
- 산화 Q와 재생된 QH가2 막으로 확산된다.
순환 전자전달
콤플렉스 III와 달리 시토크롬 bf는6 순환 광인산화 중심인 또 다른 전자전달 반응을 촉진한다.페레독신(Fd)에서 나온 전자는 플라토키노네로 옮겨진 다음 시토크롬 bf6 콤플렉스로 옮겨져 플라토시아닌을 감소시켜 포토시스템 I에서 P700에 의해 다시 산화된다.[24]페레독신에 의한 플라토키논의 감소의 정확한 메커니즘은 아직 조사 중에 있다.한 가지 제안은 페레독신:플라스토키논-감소효소 또는 NADP 탈수소효소가 존재한다는 것이다.[24]heme x는 Q 사이클에 필요한 것으로 보이지 않으며 콤플렉스 III에서는 발견되지 않기 때문에, 다음과 같은 메커니즘에 의해 주기적인 광인산화에 사용하는 것이 제안되었다.[22][25]
- Fd(빨간색) + heme x (ox) → Fd (ox) + heme x (빨간색)
- heme x (빨간색) + Fd (빨간색) + Q+ + 2H → heme x (ox) + Fd (ox) + QH2
참조
- ^ a b c Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L, Stryer L (2007). Biochemistry. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-8724-2.
- ^ a b c Hasan SS, Yamashita E, Baniulis D, Cramer WA (Mar 2013). "Quinone-dependent proton transfer pathways in the photosynthetic cytochrome b6f complex". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (11): 4297–302. doi:10.1073/pnas.1222248110. PMC 3600468. PMID 23440205.
- ^ a b Whitelegge JP, Zhang H, Aguilera R, Taylor RM, Cramer WA (Oct 2002). "Full subunit coverage liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LCMS+) of an oligomeric membrane protein: cytochrome b(6)f complex from spinach and the cyanobacterium Mastigocladus laminosus". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 1 (10): 816–27. doi:10.1074/mcp.m200045-mcp200. PMID 12438564.
- ^ a b Voet DJ, Voet JG (2011). Biochemistry. New York, NY: Wiley, J. ISBN 978-0-470-57095-1.
- ^ a b Stroebel D, Choquet Y, Popot JL, Picot D (Nov 2003). "An atypical haem in the cytochrome b(6)f complex". Nature. 426 (6965): 413–8. doi:10.1038/nature02155. PMID 14647374. S2CID 130033.
- ^ Yamashita E, Zhang H, Cramer WA (Jun 2007). "Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex: quinone analogue inhibitors as ligands of heme cn". Journal of Molecular Biology. 370 (1): 39–52. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.011. PMC 1993820. PMID 17498743.
- ^ Baniulis D, Yamashita E, Whitelegge JP, Zatsman AI, Hendrich MP, Hasan SS, Ryan CM, Cramer WA (Apr 2009). "Structure-Function, Stability, and Chemical Modification of the Cyanobacterial Cytochrome b6f Complex from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (15): 9861–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M809196200. PMC 2665108. PMID 19189962.
- ^ Hasan SS, Stofleth JT, Yamashita E, Cramer WA (Apr 2013). "Lipid-induced conformational changes within the cytochrome b6f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis". Biochemistry. 52 (15): 2649–54. doi:10.1021/bi301638h. PMC 4034689. PMID 23514009.
- ^ a b Hasan SS, Cramer WA (Jul 2014). "Internal lipid architecture of the hetero-oligomeric cytochrome b6f complex". Structure. 22 (7): 1008–15. doi:10.1016/j.str.2014.05.004. PMC 4105968. PMID 24931468.
- ^ Widger WR, Cramer WA, Herrmann RG, Trebst A (Feb 1984). "Sequence homology and structural similarity between cytochrome b of mitochondrial complex III and the chloroplast b6-f complex: position of the cytochrome b hemes in the membrane". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 81 (3): 674–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.3.674. PMC 344897. PMID 6322162.
- ^ Carrell CJ, Zhang H, Cramer WA, Smith JL (Dec 1997). "Biological identity and diversity in photosynthesis and respiration: structure of the lumen-side domain of the chloroplast Rieske protein". Structure. 5 (12): 1613–25. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00309-2. PMID 9438861.
- ^ Martinez SE, Huang D, Szczepaniak A, Cramer WA, Smith JL (Feb 1994). "Crystal structure of chloroplast cytochrome f reveals a novel cytochrome fold and unexpected heme ligation". Structure. 2 (2): 95–105. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00012-5. PMID 8081747.
- ^ Baniulis D, Yamashita E, Zhang H, Hasan SS, Cramer WA (2008). "Structure-function of the cytochrome b6f complex". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 84 (6): 1349–58. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.2008.00444.x. PMID 19067956. S2CID 44992397.
- ^ Cramer WA, Zhang H, Yan J, Kurisu G, Smith JL (May 2004). "Evolution of photosynthesis: time-independent structure of the cytochrome b6f complex". Biochemistry. 43 (20): 5921–9. doi:10.1021/bi049444o. PMID 15147175.
- ^ Hasan SS, Zakharov SD, Chauvet A, Stadnytskyi V, Savikhin S, Cramer WA (Jun 2014). "A map of dielectric heterogeneity in a membrane protein: the hetero-oligomeric cytochrome b6f complex". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 118 (24): 6614–25. doi:10.1021/jp501165k. PMC 4067154. PMID 24867491.
- ^ Munekage Y, Hashimoto M, Miyake C, Tomizawa K, Endo T, Tasaka M, Shikanai T (Jun 2004). "Cyclic electron flow around photosystem I is essential for photosynthesis". Nature. 429 (6991): 579–82. doi:10.1038/nature02598. PMID 15175756. S2CID 4421776.
- ^ Blankenship RE (2002). Molecular mechanisms of photosynthesis. Oxford ; Malden, MA: Blackwell Science. ISBN 978-0-632-04321-7.
- ^ Bendall D (1995). "Cyclic photophosphorylation and electron transport". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics. 1229: 23–38. doi:10.1016/0005-2728(94)00195-B.
- ^ Baniulis D, Hasan SS, Stofleth JT, Cramer WA (Dec 2013). "Mechanism of enhanced superoxide production in the cytochrome b(6)f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis". Biochemistry. 52 (50): 8975–83. doi:10.1021/bi4013534. PMC 4037229. PMID 24298890.
- ^ Hasan SS, Proctor EA, Yamashita E, Dokholyan NV, Cramer WA (Oct 2014). "Traffic within the cytochrome b6f lipoprotein complex: gating of the quinone portal". Biophysical Journal. 107 (7): 1620–8. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2014.08.003. PMC 4190601. PMID 25296314.
- ^ Cramer WA, Soriano GM, Ponomarev M, Huang D, Zhang H, Martinez SE, Smith JL (Jun 1996). "Some New Structural Aspects and Old Controversies Concerning the Cytochrome b6f Complex of Oxygenic Photosynthesis". Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology. 47: 477–508. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.477. PMID 15012298.
- ^ a b Cramer WA, Zhang H, Yan J, Kurisu G, Smith JL (2006). "Transmembrane traffic in the cytochrome b6f complex". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 75: 769–90. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142756. PMID 16756511.
- ^ Malone LA, Qian P, Mayneord GE, Hitchcock A, Farmer DA, Thompson RF, et al. (November 2019). "Cryo-EM Structure of the Spinach Cytochrome B 6 F Complex at 3.6 Å Resolution" (PDF). Nature. 575 (7783): 535–539. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1746-6. PMID 31723268. S2CID 207987984.
- ^ a b Joliot P, Joliot A (Jul 2002). "Cyclic electron transfer in plant leaf". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (15): 10209–14. doi:10.1073/pnas.102306999. PMC 126649. PMID 12119384.
- ^ Cramer WA, Yan J, Zhang H, Kurisu G, Smith JL (2005). "Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex: new prosthetic groups, Q-space, and the 'hors d'oeuvres hypothesis' for assembly of the complex". Photosynthesis Research. 85 (1): 133–43. doi:10.1007/s11120-004-2149-5. PMID 15977064. S2CID 20731696.
외부 링크
- 시토크롬 bf6 복합체의 구조기능 연구 - 미국 퍼듀대학 윌리엄 크래머 연구소의 시토크롬 bf에6 관한 연구
- IMT-2000 3GPP-막 제품군 내 단백질의 UMICH 방향-3 - b6f와 막 내 관련 복합체의 계산된 위치
- Cytochrome+b6f+Complex(미국 국립 의학 라이브러리 의료 과목 제목)



