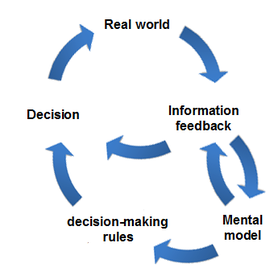
이중 루프 학습
Double-loop learning이중 루프 학습은 경험에 비추어 목표나 의사결정 규칙의 수정을 수반한다. 첫 번째 루프는 목표나 의사결정 규칙을 사용하고, 두 번째 루프는 목표의 수정을 가능하게 하므로 "이중 루프"이다. 이중 루프 학습은 문제를 정의하고 해결하는 방법이 문제의 근원이 될 수 있다는 것을 인식한다.[1] 이러한 유형의 학습은 변화에 적응하는 것을 넘어 변화에 대한 예측이나 변화에 앞서가는 것을 넘어 창의성과 혁신을 주도할 수 있기 때문에 조직 학습에 유용할 수 있다.[2]
개념
이중 루프 학습은 "단일 루프 학습"과 대조되는데, 동일한 문제에 대해 반복적으로 시도하며, 방법의 변화가 없고 목표에 대해 의문을 제기하지 않는다. Chris Argyris는 다음과 같은 비유를 사용하여 단일 루프 학습과 이중 루프 학습의 구별을 설명했다.
실내 온도가 68°F 이하로 떨어질 때마다 자동으로 불을 켜는 [A] 서모스탯이 단루프 학습의 좋은 예다. "왜 내가 68°F로 설정되었는가?"라고 물어본 후 다른 온도가 실내 난방 목표를 더 경제적으로 달성할 수 있는지 여부를 탐색할 수 있는 온도 조절기
이중 루프 학습은 결정이 의존하는 정신적 모델을 변경할 필요가 있을 때 사용된다. 이 모델은 단일 루프와는 달리 단순하고 정적인 것에서 주변 환경의 변화, 정신적 모델의 표현 변화의 필요성을 고려하는 등 보다 광범위하고 역동적인 이해의 전환을 포함한다.[3] 조직 학습 과정을 시작하는 문제나 불일치가 조직의 통치 변수를 수반하기 때문에 작은 조정으로 해결할 수 없는 경우 필요하다.[4] 이러한 경우에 조직적 학습은 진단과 개입이 기본 정책, 가정 및 목표에 변화를 일으킬 때 발생한다.[5] 아르기리스에 따르면 변화에 대한 저항, 실패에 대한 두려움, 통제에 대한 지나친 강조 등 여러 변수로 인해 많은 조직이 이중 루프 학습에 저항하고 있다.[6]
- 참조 모델 I 및 II
역사적 전구체
회사의 행동 이론(1963)은 조직이 (지금 설명될 것은) 이중 루프 학습을 사용하여 배우는 방법을 설명한다.
조직은... 상당히 잘 정의된 규칙에 따라 환경의 단기적인 피드백에 대응하여 행동을 변화시킨다. 더 일반적인 규칙 등에 따라 더 오래 실행되는 피드백에 대응하여 규칙을 변경한다.
참고 항목
참조
- ^ a b Argyris, Chris (May 1991). "Teaching smart people how to learn" (PDF). Harvard Business Review. 69 (3): 99–109. Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ^ Malone, Samuel A. (2003). Learning about Learning. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. p. 80. ISBN 0852929897. OCLC 52879237.
- ^ Mildeova, S., Vojtko V. (2003). Systémová dynamika (in Czech). Prague: Oeconomica. pp. 19–24. ISBN 978-80-245-0626-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint : 복수이름 : 작성자 목록(링크) - ^ Horst, Hilde ter; Mulder, Martin; Sambrook, Sally; Scheerens, Jaap; Stewart, Jim; Tjepkema, Saskia, eds. (2002). HRD and Learning Organisations in Europe. Routledge studies in human resource development. Vol. 3. London; New York: Routledge. p. 8. ISBN 0415277884. OCLC 49350862.
- ^ Rahim, M. Afzalur (2001). Managing Conflict in Organizations (3 ed.). Westport, CT: Quorum Books. p. 64. ISBN 1567202624. OCLC 45791568.
- ^ Bess, James L.; Dee, Jay R. (2008). Understanding College and University Organization: Theories for Effective Policy and Practice. Vol. 2. Stylus Publishing. p. 676. ISBN 9781579227746. OCLC 73926579.
- ^ Cyert R.M.; March J.G. (1963). A Behavioral Theory of the Firm. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall. pp. 101–102.
- ^ 이 인용구를 "단일 학습과 이중 루프 학습의 구별의 초기 버전"으로 설명하고 1963년 판을 참조하는 조직 학습 및 지식 관리의 블랙웰 핸드북(2003)의 9페이지에서 인용한 것이다.
추가 읽기
- Bassot, Barbara (2015). "Bringing assumptions to the surface". The reflective practice guide: an interdisciplinary approach to critical reflection. Abingdon; New York: Routledge. pp. 79–92. ISBN 9781138784307. OCLC 898925915.
- Bochman, David J.; Kroth, Michael (2010). "Immunity to transformational learning and change". The Learning Organization. 17 (4): 328–342. doi:10.1108/09696471011043090.
- Fraser, J. Scott; Solovey, Andrew D. (2007). Second-order change in psychotherapy: the golden thread that unifies effective treatments. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ISBN 978-1591474364. OCLC 65195322.
- Brockbank, Anne; McGill, Ian (2012) [2006]. "Single and double loop learning". Facilitating reflective learning: coaching, mentoring and supervision (2nd ed.). London; Philadelphia: Kogan Page. pp. 22–26. ISBN 9780749465070. OCLC 769289635.
- Argyris, Chris (2005). "Double-loop learning in organizations: a theory of action perspective". In Smith, Ken G.; Hitt, Michael A. (eds.). Great minds in management: the process of theory development. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 261–279. ISBN 978-0199276813. OCLC 60418039.
- Blackman, Deborah; Connelly, James; Henderson, Steven (January 2004). "Does double loop learning create reliable knowledge?". The Learning Organization. 11 (1): 11–27. doi:10.1108/09696470410515706. S2CID 144174842.
- Torbert, William R.; Cook-Greuter, Susanne R.; Fisher, Dalmar; Foldy, Erica; Gauthier, Alain; Keeley, Jackie; Rooke, David; Ross, Sara Nora; Royce, Catherine; Rudolph, Jenny (2004). Action inquiry: the secret of timely and transforming leadership. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler. ISBN 978-1576752647. OCLC 53793296.
- Smith, Mark K. (2013) [2001]. "Chris Argyris: theories of action, double-loop learning and organizational learning". infed.org. Retrieved 2016-03-19.
- Nielsen, Richard P. (1996). "Double-loop, dialogue methods". The politics of ethics: methods for acting, learning, and sometimes fighting with others in addressing ethics problems in organizational life. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 75–105. ISBN 978-0195096651. OCLC 34517566.
- Argyris, Chris (1999) [1993]. On organizational learning (2nd ed.). Oxford; Malden, MA: Blackwell Business. ISBN 978-0631213086. OCLC 40460132.
- Isaacs, William N. (September 1993). "Taking flight: dialogue, collective thinking, and organizational learning" (PDF). Organizational Dynamics. 22 (2): 24–39. doi:10.1016/0090-2616(93)90051-2.
- Argyris, Chris (1980). Inner contradictions of rigorous research. Organizational and occupational psychology. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0120601509. OCLC 6421943.
- Argyris, Chris; Schön, Donald A. (1978). Organizational learning: a theory of action perspective. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0201001747. OCLC 394956102.
- Argyris, Chris (September 1976). "Single-loop and double-loop models in research on decision making". Administrative Science Quarterly. 21 (3): 363–375. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.463.4908. doi:10.2307/2391848. JSTOR 2391848.