엑세컨트
Exsecant| 삼각법 |
|---|
 |
| 참조 |
| 법과 정리 |
| 미적분학. |
Exsecant(exsec, exc)와 excosecant(exc, exc, exc)는 secant 및 cosecant 함수에 대해 정의된 삼각함수다. 그것들은 측량, 철도 공학, 토목 공학, 천문학, 구면 삼각법과 같은 분야에서 중요했고 정확도 향상에 도움이 될 수 있었지만, 오늘날에는 일부 계산을 단순화하는 것 외에는 거의 사용되지 않는다.
엑세컨트
외부, 외부,[14][15][16][17] 외부, 외부 또는 외부 세컨트로 알려져 있고 exsec[18][19][20][21] 또는 exs로 약칭되는 Exsecant([2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9]라틴어: secans[10][11][12][13] 외부)는 다음 세컨트 함수 sec(sec)의 관점에서 정의된 삼각 함수다.[22][23]
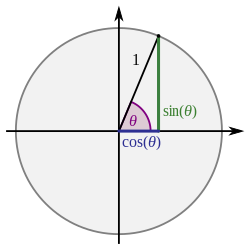
exsecant라는 이름은 역사적으로 사용되었던 것과 같이 단위 원으로부터 다양한 삼각함수의 그래픽 구조를 통해 이해할 수 있다. sec(second)는 secant line OE이며, exsecant는 원 외부에 있는 이 secant의 부분 DE이다(ex는 out의 경우 라틴어임).
엑소세칸트
관련 함수는 외부[5][24], 외부,[17] 외부 또는 외부 코섹트라고도 하며 보완 각도의 Excosec, [22]coosec,[14][18][26] exsc[5][24] 또는 exc로 약칭된다.[25][18][26]
사용법
1980년대까지 측량,[8] 철도 공학[5](예를 들어 철도 곡선 및 편경사를 배치하는 것), 토목 공학, 천문학, 구면 삼각법과 같은 분야에서 중요했던, 제외 기능은 현재 거의 사용되지 않고 있다.[8][23] 주로 계산기와 컴퓨터의 폭넓은 가용성으로 인해 이것과 같은 특화된 기능의 삼각표 필요성이 없어졌기 때문이다.[8]
엑세컨트에 대한 특수 함수를 정의해야 하는 이유는 버시네에 대한 이론적 근거와 유사하다: 작은 각도 θ에 대해서는 sec(sec) 함수가 1에 근접하기 때문에 엑세컨트에 대해 위의 공식을 사용하는 것은 거의 동일한 두 양의 뺄셈을 수반하게 되어 치명적인 해소를 초래하게 된다. 따라서 제2차 함수의 표는 제2차 함수에 사용하기 위해 매우 높은 정확도를 필요로 하므로 전문 제2차 함수의 표는 유용하다. 컴퓨터가 있더라도 코사인 기반 정의를 사용하면 작은 각도의 외부인에게 부동소수점 오류가 문제가 될 수 있다. 이 한계에서 더 정확한 공식은 다음과 같은 정체성을 사용하는 것이다.
또는
컴퓨터를 이용하기 전에, 이것은 시간이 많이 걸리는 배수를 필요로 할 것이다.
구세컨트 함수는 1632년 갈릴레오 갈릴레이가 여전히 세간테(secante를 의미함)라고 불렀지만 이미 사용하였다.[27][28][29][30] 라틴어 secans 외관은 적어도 1745년경부터 사용되었다.[10][11][12][13] 영어 용어인 외부 세컨트와 약어 ex.sec의 사용은 찰스 해슬렛이 처음으로 알려진 국외 추방자 표를 발표했을 때 가장 적은 1855년으로 거슬러 올라갈 수 있다.[1][31] 1880년에는 ex secant와 exsec과 같은 변형이 사용되었고,[14] 1894년부터 exsecant가 가장 적게 사용되었다.[2]
코엑스칸트와[25] 코엑스섹이라는[2] 용어는 이르면 1880년에 쓰일[2][25] 수 있으며 1909년 이후부터 흥분제라는 용어가 뒤따른다.[5] 이 기능은 페르미온의 운동 에너지를 설명하기 위해 알버트 아인슈타인에 의해서도 이용되었다.[29][30]
수학적 정체성
파생상품
통합
역함수
역함수 아르섹스칸트[26](arcexsec,[5][26] aexsec,[32][33] aexec, execs, exec−1)와 아르섹스칸트(arcexcosec, arcexcsc,[5] aexsc, aexcecant, arcoexsec, exsc−1)도 존재한다.
기타 속성
단위 원으로부터 파생됨:
Exsecant 함수는 다음에 의해 접선 함수와 관련된다.
유추하여, 흥분함수는 다음과 같이 코탄젠트 함수와 관련이 있다.
Exsecant 함수는 다음에 의해 사인 함수와 관련된다.
유사하게, 배설함수는 코사인 함수에 의해 관련된다.
Exsecant 및 excosecant 기능은 복잡한 평면까지 확장할 수 있다.[21]
참고 항목
- 삼각측량 ID – 삼각함수를 포함하는 동일성
- Versine – 1에서 각도의 코사인 빼기
- 현 – 끝점이 모두 곡선에 있는 기하학적 선 세그먼트
- 삼각형의 근골과 외골 – 삼각형의 세 면 모두에 접하는 원
- 지수 마이너스 1
- 자연 로그 플러스 1
참조
- ^ a b Haslett, Charles (September 1855). Hackley, Charles W. (ed.). The Mechanic's, Machinist's, Engineer's Practical Book of Reference: Containing tables and formulæ for use in superficial and solid mensuration; strength and weight of materials; mechanics; machinery; hydraulics, hydrodynamics; marine engines, chemistry; and miscellaneous recipes. Adapted to and for the use of all classes of practical mechanics. Together with the Engineer's Field Book: Containing formulæ for the various of running and changing lines, locating side tracks and switches, &c., &c. Tables of radii and their logarithms, natural and logarithmic versed sines and external secants, natural sines and tangents to every degree and minute of the quadrant, and logarithms from the natural numbers from 1 to 10,000. New York, USA: James G. Gregory, successor of W. A. Townsend & Co. (Stringer & Townsend). Retrieved 2017-08-13.
[…] Still there would be much labor of computation which may be saved by the use of tables of external secants and versed sines, which have been employed with great success recently by the Engineers on the Ohio and Mississippi Railroad, and which, with the formulas and rules necessary for their application to the laying down of curves, drawn up by Mr. Haslett, one of the Engineers of that Road, are now for the first time given to the public. […] In presenting this work to the public, the Author claims for it the adaptation of a new principle in trigonometrical analysis of the formulas generally used in field calculations. Experience has shown, that versed sines and external secants as frequently enter into calculations on curves as sines and tangents; and by their use, as illustrated in the examples given in this work, it is believed that many of the rules in general use are much simplified, and many calculations concerning curves and running lines made less intricate, and results obtained with more accuracy and far less trouble, than by any methods laid down in works of this kind. The examples given have all been suggested by actual practice, and will explain themselves. […] As a book for practical use in field work, it is confidently believed that this is more direct in the application of rules and facility of calculation than any work now in use. In addition to the tables generally found in books of this kind, the author has prepared, with great labor, a Table of Natural and Logarithmic Versed Sines and External Secants, calculated to degrees, for every minute; also, a Table of Radii and their Logarithms, from 1° to 60°. […]
1856년 판 - ^ a b c d Allen, Calvin Frank (1894) [1889]. Railroad Curves and Earthwork. New York, USA; London, UK: Spon & Chamberlain; E. & F. Spon, Ltd. Retrieved 2015-11-16.
- ^ a b Nagle, James C. (1897). "IV.138.-165.: Transition Curves; Table XIII.: Natural Versines and Exsecants". Field Manual for Railroad Engineers (1 ed.). New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons, Chapman and Hall, Limited. pp. 110–142, 332–354. Retrieved 2015-11-16.
- ^ a b "Field Manual for Railroad Engineers" (PDF). The Engineer (Review): 540. 1897-12-03. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-11-17. Retrieved 2015-11-17.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Hall, Arthur Graham; Frink, Fred Goodrich (January 1909). "Review Exercises [100] Secondary Trigonometric Functions". Written at Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA. Trigonometry. Part I: Plane Trigonometry. New York, USA: Henry Holt and Company / Norwood Press / J. S. Cushing Co. - Berwick & Smith Co., Norwood, Massachusetts, USA. p. 125. Retrieved 2017-08-12.
- ^ Boyer, Carl Benjamin (1969) [1959]. "5: Commentary on the Paper of E. J. Dijksterhuis (The Origins of Classical Mechanics from Aristotle to Newton)". In Clagett, Marshall (ed.). Critical Problems in the History of Science (3 ed.). Madison, Milwaukee, and London: University of Wisconsin Press, Ltd. pp. 185–190. ISBN 0-299-01874-1. LCCN 59-5304. 9780299018740. Retrieved 2015-11-16.
- ^ Zucker, Ruth (1983) [June 1964]. "Chapter 4.3.147: Elementary Transcendental Functions - Circular functions". In Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene Ann (eds.). Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. Applied Mathematics Series. 55 (Ninth reprint with additional corrections of tenth original printing with corrections (December 1972); first ed.). Washington D.C.; New York: United States Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards; Dover Publications. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-486-61272-0. LCCN 64-60036. MR 0167642. LCCN 65-12253.
- ^ a b c d Calvert, James B. (2007-09-14) [2004-01-10]. "Trigonometry". Archived from the original on 2007-10-02. Retrieved 2015-11-08.
- ^ Tapson, Frank (2004). "Background Notes on Measures: Angles". 1.4. Cleave Books. Archived from the original on 2007-02-09. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
- ^ a b Patu, Andræâ-Claudio (André Claude); Le Tort, Bartholomæus (February 1745). Rivard, Franciscus (Dominique-François) (ed.). Theses Mathematicæ De Mathesi Generatim (in Latin). Collegio Dormano–Bellovaco (Collège de Dormans–Beauvais), Paris: Ph. N. Lottin. p. 6. Retrieved 2017-08-06.
- ^ a b Lemonnier, Petro (Pierre) (1750). Genneau, Ludovicum (Ludovico); Rollin, Jacobum (Jacques) (eds.). Physica generalis. Cursus Philosophicus Ad Scholarum Usum Accomodatus (in Latin). 3. Collegio Harcuriano (Collège d'Harcourt), Paris. pp. 303–. Retrieved 2017-08-06.
- ^ a b Thysbaert, Jan-Frans (1774). "Articulus II: De situ lineæ rectæ ad Circularem; & de mensura angulorum, quorum vertex non est in circuli centro. §1. De situ lineæ rectæ ad Circularem. Definitio II: [102]". Geometria elementaria et practica (in Latin). Lovanii, e typographia academica. p. 30, foldout. Retrieved 2017-08-06.
- ^ a b van Haecht, Joannes (1784). "Articulus III: De secantibus circuli: Corollarium III: [109]". Geometria elementaria et practica: quam in usum auditorum (in Latin). Lovanii, e typographia academica. p. 24, foldout. Retrieved 2017-08-06.
- ^ a b c Searles, William Henry (1880-03-01). Field Engineering - A Hand-book of the Theory and Practice of Railway Surveying, Location, and Construction, designed for the Class-room, Field and Office, and containing a large number of useful tables, original and selected (PDF). New York, USA: John Wiley & Sons. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-13. Retrieved 2017-08-13. 제8회 개정판, 1887년 1910년 16월호
- ^ Cajori, Florian (1952) [March 1929]. A History of Mathematical Notations. 2 (2 (3rd corrected printing of 1929 issue) ed.). Chicago, USA: Open court publishing company. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-60206-714-1. 1602067147. Retrieved 2015-11-11. (NB. ISBN 및 2013년 미국 뉴욕주 코시모사의 2판 재인쇄 링크)
- ^ Swanson, Todd; Andersen, Janet; Keeley, Robert (1999). "5 (Trigonometric Functions)" (PDF). Precalculus: A Study of Functions and Their Applications. Harcourt Brace & Company. p. 344. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2003-06-17. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
- ^ a b c d Gottschalk, Walter Helbig (2002). Some Quaint & Curious & Almost Forgotten Trig Functions (PDF). Gottschalk's Gestalts - A Series Illustrating Innovative Forms of the Organization & Exposition of Mathematics. 80. Providence, Rhode Island, USA: Infinite Vistas Press. PVD RI, GG80. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-09-25. Retrieved 2015-11-17.
- ^ a b c Frye, Albert I. (1918) [1913]. Civil engineer's pocket-book: a reference-book for engineers, contractors and students containing rules, data, methods, formulas and tables (2 (corrected) ed.). New York, USA; London, UK: D. Van Nostrand Company; Constable and Company, Ltd. Retrieved 2015-11-16.
- ^ Kenyon, Alfred Monroe; Ingold, Louis (1913). Trigonometry. New York, USA: The Macmillan Company. p. 5. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- ^ Hudson, Ralph Gorton; Lipka, Joseph (1917). A Manual of Mathematics. New York, USA: John Wiley & sons. p. 68. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- ^ a b c d Weisstein, Eric Wolfgang (2015) [2005]. "Exsecant". MathWorld. Wolfram Research, Inc. Archived from the original on 2005-11-29. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- ^ a b Shaneyfelt, Ted V. "德博士的 Notes About Circles, ज्य, & कोज्य: What in the world is a hacovercosine?". Hilo, Hawaii: University of Hawaii. Archived from the original on 2015-09-19. Retrieved 2015-11-08.
- ^ a b c Oldham, Keith B.; Myland, Jan C.; Spanier, Jerome (2009) [1987]. "33.13. The Secant sec(x) and Cosecant csc(x) functions - Cognate functions". An Atlas of Functions: with Equator, the Atlas Function Calculator (2 ed.). Springer Science+Business Media, LLC. p. 336. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-48807-3. ISBN 978-0-387-48806-6. LCCN 2008937525.
- ^ a b c Weisstein, Eric Wolfgang (2015) [2013]. "Excosecant". MathWorld. Wolfram Research, Inc. Archived from the original on 2014-03-26. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- ^ a b c Bohannan, Rosser Daniel (1904) [1903]. "$131. The Versed Sine, Exsecant and Coexsecant. §132. Exercises". Plane Trigonometry. Ohio State University: Allyn and Bacon, Boston, USA / J. S. Cushing & Co. — Berwick & Smith Co., Norwood, MA. pp. 235–236. Retrieved 2017-07-09.
- ^ a b c d e f van Vlijmen, Oscar (2005-12-28) [2003]. "Goniology". Eenheden, constanten en conversies. Archived from the original on 2009-10-28. Retrieved 2015-11-28.
- ^ Galilei, Galileo (1632). Dialogo di Galileo Galilei sopra i due massimi sistemi del mondo Tolemaico e Copernicano [Dialogue on the Two Chief World Systems, Ptolemaic and Copernican] (in Italian).
- ^ Galilei, Galileo (1997-05-25) [1632]. Finocchiaro, Maurice A. (ed.). Galileo on the World Systems: A New Abridged Translation and Guide. University of California Press. pp. 184 (n130), 184 (n135), 192 (n158). ISBN 9780520918221. Retrieved 2017-07-30.
[…] Galileo's word is segante (meaning secant), but he clearly intends exsecant; an exsecant is defined as the part of a secant external to the circle […]
- ^ a b Hawking, Stephen William, ed. (2002). On the Shoulders of Giants: The Great Works of Physics and Astronomy. Philadelphia, USA: Running Press. ISBN 0-7624-1698-X. LCCN 2002100441. Retrieved 2017-07-31.
- ^ a b c Stávek, Jiří (2017-03-10) [2017-02-26]. "On the Hidden Beauty of Trigonometric Functions". Applied Physics Research. Prague, CZ: Canadian Center of Science and Education. 9 (2): 57–64. doi:10.5539/apr.v9n2p57. ISSN 1916-9639. ISSN 1916-9647. [1]
- ^ Poor, Henry Varnum, ed. (1856-03-22). "PRACTICAL BOOK OF REFERENCE, and Engineer's Field Book. By Charles Haslett, C.E. Edited by Professor Charles W. Hackley, 1 vol. 12mo. Pp. 617. Prico $2.50. Columbia College, N. Y. Stringer & Townsend" (PDF). American Railroad Journal - Steam Navigation, Commerce, Mining, Manufacturers (Review). Second Quarto Series. J. H. Schultz & Co. XII (12): 184. Whole No. 1040, Vol. XX. Retrieved 2017-08-14.
- ^ a b Simpson, David G. (2001-11-08). "AUXTRIG" (Fortran 90 source code). Greenbelt, Maryland, USA: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Archived from the original on 2008-06-16. Retrieved 2015-10-26.
- ^ a b van den Doel, Kees (2010-01-25). "jass.utils Class Fmath". JASS - Java Audio Synthesis System. 1.25. Archived from the original on 2007-09-02. Retrieved 2015-10-26.









![\int \operatorname {exsec} (\theta )\,\mathrm {d} \theta =\ln \left[\cos \left({\frac {\theta }{2}}\right)+\sin \left({\frac {\theta }{2}}\right)\right]-\ln \left[\cos \left({\frac {\theta }{2}}\right)-\sin \left({\frac {\theta }{2}}\right)\right]-\theta +C](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4023beda8fb65a34b16efb3b5d4ca17302b8b82e)
![{\displaystyle \int \operatorname {excsc} (\theta )\,\mathrm {d} \theta =\ln \left[\tan \left({\frac {\theta }{2}}\right)\right]-\theta +C}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/38a6dcd03b3efddd2ef0bb822bf70f9505556913)
















