ERX-11
ERX-11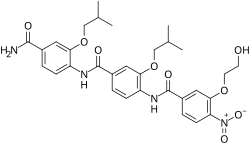 | |
| 임상 데이터 | |
|---|---|
| 기타 이름 | ERα 코어 조절기 결합 변조기-11 |
| 루트 행정부. | 입으로[1][2] |
| 식별자 | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| 화학 및 물리 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C31H36N4O9 |
| 몰 질량 | 608.648 g/g−1/g |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
ERX-11은 에스트로겐 수용체 양성 유방암의 잠재적 치료를 위해 연구되고 있는 새로운 항에스트로겐 [1][2]및 실험 호르몬 항종양제이다.ER의 리간드 결합 부위에 결합하는 대신 ERX-11은 ERα의 다른 부분과 상호작용하고 ERα의 단백질-단백질 상호작용을 차단하여 수용체가 작용하는 데 필요한 핵심 조절제와의 ERα의 단백질-단백질 상호작용을 차단한다.유전자 [1][2]발현을 조절합니다.ERα의 코어 조절기 결합 영역에 결합하고 ERα/공활성제 상호작용을 억제하도록 설계되었지만, 정확한 결합 부위와 작용 모드는 아직 완전히 설명되고 [1][2][3][4]이해되지 않았습니다.단, ERX-11이 ERα의 [1]AF-2 도메인 내에 결합하는 것은 분명하다.
ERX-11은 경구활성 [1][2]소분자 트리벤자미드 화합물로, 치료용량보다 훨씬 높은 용량에서도 체외에서 양호한 항에스트로겐 효력과 생체 내 독성 징후가 최소화된다.이 화합물은 핵 수용체 결합 모티브를 모방하여 ERα와 그 공활성제의 [1][2]상호작용에 중요한 것으로 보인다.그것은 ERα과 91ERα-binding coregulators 사이에 SRC1, SRC3, PELP1을 포함한 상호 작용을 방해할 수 있다.[1][2]ERX-11 8개ER-positive 유방 암 세포주 중에서 IC50 값 250nM과 500nM,도fulvestranttamoxifen은 ZR-75과 MCF-7 brea의 성장 억제에 효과적인 간의 범위를 가진 estradiol-induced 확산 저지했다.성암 [1][2]세포주.그것은 ER 음성 유방암 [1][2]세포주에서는 활성화되지 않았다.
타목시펜 및 풀베스트란트 같은 기존 항에스트로겐과 달리 ERX-11은 치료 민감성 [1][2]및 치료 내성 유방암 세포에서 ER 신호뿐만 아니라 리간드 의존성 및 리간드 비의존성 ER 신호 모두를 차단하는 것으로 밝혀졌다.또한 ERα와 타목시펜과 같은 기존 항에스트로겐의 영향을 받지 않는 많은 ERα 결합 코어조절기(단백질 88개 중 33개, 37.5%)[1][2] 사이의 상호작용을 방해했다.그것은 또한 [1][2]타목시펜과 달리 유방암 세포에서 아포토시스를 유발했다.인체 임상시험에서 [2]ERX-11을 평가하기 위한 노력이 진행 중이다.
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Raj GV, Sareddy GR, Ma S, Lee TK, Viswanadhapalli S, Li R, Liu X, Murakami S, Chen CC, Lee WR, Mann M, Krishnan SR, Manandhar B, Gonugunta VK, Strand D, Tekmal RR, Ahn JM, Vadlamudi RK (August 2017). "Estrogen receptor coregulator binding modulators (ERXs) effectively target estrogen receptor positive human breast cancers". eLife. 6. doi:10.7554/eLife.26857. PMC 5548489. PMID 28786813.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Ekoue DN, Unni N, Raj GV (April 2018). "A new class of agents for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer". Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 11 (4): 325–328. doi:10.1080/17512433.2018.1439736. PMID 29439601.
- ^ Qin, Weirong; Xie, Mingsheng; Qin, Xuan; Fang, Qi; Yin, Feng; Li, Zigang (2018). "Recent Advances in Peptidomimetics Antagonists Targeting Estrogen Receptor α-Coactivator Interaction in Cancer Therapy". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 28 (17): 2827–2836. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.05.062. ISSN 0960-894X. PMID 30025900. S2CID 51702195.
In 2017, Raj et al. reported a small molecule compound 12, which was the most well-characterized small molecule for inhibiting ERα-coactivator interaction.50 Compound 12 is a tri-benzamide that could inhibit the proliferation of several different ERα-positive breast cancer cells. Notably, it could regress the growth of ERα-positive breast cancer xenograft in vivo. 12 was designed to bind to the coactivator binding groove of ERα, but the mode of action and precise binding site were not fully elucidated yet.
- ^ Speltz TE, Danes JM, Stender JD, Frasor J, Moore TW (March 2018). "A Cell-Permeable Stapled Peptide Inhibitor of the Estrogen Receptor/Coactivator Interaction". ACS Chem. Biol. 13 (3): 676–684. doi:10.1021/acschembio.7b01016. PMC 6057476. PMID 29309722.
The most well-characterized molecule for inhibiting the ER/coregulator interaction comes from Raj et al., who recently described ERX-11, a small molecule that is active in several different models of ER+ breast cancer, including a tumor xenograft model.18 ERX-11 is an oligoamide that was designed to bind to ER at the coregulator-binding region, but even after careful experimentation and design, the precise binding site and mode of action is not fully understood for ERX-11, demonstrating the difficult nature of designing inhibitors of this protein−protein interaction.


