스테폴리딘
Stepholidine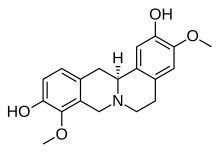 | |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC 이름 3,9-디메트호시베르빈-2,10-다이올 | |
| 선호 IUPAC 이름 (13aS)-3,9-디메트호시-5,8,13,13a-테트라하이드로-6H-isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline-2,10-diol | |
| 기타 이름 l-스텝홀리딘 | |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 켐벨 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 메슈 | 스테폴리딘 |
펍켐 CID | |
| 유니 | |
CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| 특성. | |
| C19H21NO4 | |
| 어금질량 | 327.374 g/190 |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하고, 표준 상태(25°C [77°F], 100 kPa)의 재료에 대한 데이터가 제공된다. | |
| Infobox 참조 자료 | |
(--Stepholidine은 스테파니아 인터미디어 식물에서 발견되는 프로토베르베린 알칼로이드다.
스테폴리딘 활성은 이중 D2 수용체 길항제 및 D1 수용체 작용제를 포함하며 동물 연구에서 항정신병 활성을 보였다.[1][2][3][4]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ Natesan S, Reckless GE, Barlow KB, et al. (August 2008). "The antipsychotic potential of l-stepholidine-a naturally occurring dopamine receptor D(1) agonist and D (2) antagonist". Psychopharmacology. 199 (2): 275–89. doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1172-1. PMID 18521575. S2CID 21653956.
- ^ Mo J, Guo Y, Yang YS, Shen JS, Jin GZ, Zhen X (2007). "Recent developments in studies of l-stepholidine and its analogs: chemistry, pharmacology and clinical implications". Curr. Med. Chem. 14 (28): 2996–3002. doi:10.2174/092986707782794050. PMID 18220736.
- ^ Jin GZ, Zhu ZT, Fu Y (January 2002). "(-)-Stepholidine: a potential novel antipsychotic drug with dual D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist actions". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 23 (1): 4–7. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01929-5. PMID 11804640.
- ^ Fu W, Shen J, Luo X, et al. (September 2007). "Dopamine D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist effects of the natural product (-)-stepholidine: molecular modeling and dynamics simulations". Biophys. J. 93 (5): 1431–41. doi:10.1529/biophysj.106.088500. PMC 1948031. PMID 17468175.


