척추압박골절
Vertebral compression fracture| 압축파단 | |
|---|---|
 | |
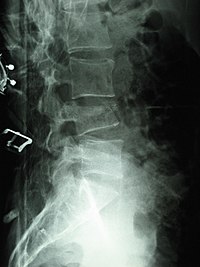
| 척추압박골절의 예 | |
| 전문 | 정형외과 |
압박골절은 척추의 붕괴다. 외상 때문일 수도 있고 척추의 약화 때문일 수도 있다(파열골절과 비교). 이러한 약화는 골다공증이나 골형성 불완전성, 전이성 또는 1차 종양으로 인한 용액성 병변 [1]또는 감염증 환자에게서 나타난다.[2] 건강한 환자들에게, 그것은 배출 좌석에서 배출되는 것과 같은 극단적인 수직적 충격을 받는 사람들에게서 가장 흔히 나타난다. 평이한 X선 필름의 측면 시야에서 볼 수 있는 척추의 압축 골절은 특징적으로 쐐기 기형으로 나타나며, 후측 및 온전한 안테로포스테리어 시야에서 전측 키 손실이 크다.[3]
징후 및 증상
급성 골절은 심한 요통을 일으킬 것이다. 골다공증처럼 점차적으로 발달하는 압박골절은 처음에는 아무런 증상을 일으키지 않을 수 있지만, 나중에는 요통과 키의 상실로 이어지는 경우가 많다.[citation needed]
진단
압박골절은 보통 척추방사선에서 진단하는데, 쐐기 모양의 척추뼈가 보이거나 척추 높이 손실이 있을 수 있다. 또한 골다공증에 대한 평가를 위해 골밀도 측정을 수행할 수 있다. 종양이 근본적인 원인으로 의심되거나 심한 외상으로 인해 골절이 발생한 경우 CT나 MRI 촬영을 실시할 수 있다.[citation needed]
치료
보수적 대우
- 뼈가 치유되는 동안 뒷받침을 위한 등받이 버팀대 - 비교적 안정적이고 가벼운 부상의 경우 Jujett 가새 또는 더 심각한 부상의 경우 흉부 요추 천골 정사(TLSO)[5]
- 통증을 위한 오피오이드 또는 비스테로이드성 소염제(NSAIDs) 골다공증 환자에게는 칼시토닌이 도움이 될 수 있다.[6][7]
외과적
참조
- ^ Weber, Kristy (February 28, 2006). "Rounds 2: Treatment of Metastatic Bone Disease". Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center.
- ^ "Bone Infections". MedlinePlus. September 7, 2011.
- ^ Brant, William E.; Helms, Clyde A. (2007). "Benign Compression Fracture". Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 302. ISBN 978-0-7817-6135-2.
- ^ Freedman, B. A.; Heller, J. G. (2009). "Kummel Disease: A Not-So-Rare Complication of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures". The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. 22 (1): 75–78. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.01.080100. ISSN 1557-2625. PMID 19124637.
- ^ "Jewett vs. TLSO Replies". OANDP-L on oandp.com. 2010-09-27. Retrieved 2012-09-02.
- ^ "Calcitonin for osteoporotic fractures". Archived from the original on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
- ^ Knopp, Jennifer A.; Diner, Barry M.; Blitz, Maurice; Lyritis, George P.; Rowe, Brian H. (2004). "Calcitonin for treating acute pain of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A systematic review of randomized, controlled trials". Osteoporosis International. 16 (10): 1281–90. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1798-8. PMID 15614441. S2CID 34208503.
- ^ a b Taylor, Rod S.; Taylor, Rebecca J.; Fritzell, Peter (2006). "Balloon Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Vertebral Compression Fractures". Spine. 31 (23): 2747–55. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000244639.71656.7d. PMID 17077747. S2CID 209491.
- ^ Taylor, Rod S.; Fritzell, Peter; Taylor, Rebecca J. (2007). "Balloon kyphoplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis". European Spine Journal. 16 (8): 1085–100. doi:10.1007/s00586-007-0308-z. PMC 2200787. PMID 17277923.
- ^ Boonen, S.; Wahl, D. A.; Nauroy, L.; Brandi, M. L.; Bouxsein, M. L.; Goldhahn, J.; Lewiecki, E. M.; Lyritis, G. P.; et al. (2011). "Balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures". Osteoporosis International. 22 (12): 2915–34. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1639-5. PMID 21789685. S2CID 19967779.
- ^ Han, Shiliang; Wan, Shuanglin; Ning, Lei; Tong, Yongjun; Zhang, Jianfeng; Fan, Shunwu (2011). "Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised controlled trials". International Orthopaedics. 35 (9): 1349–58. doi:10.1007/s00264-011-1283-x. PMC 3167445. PMID 21637959.
추가 읽기
| 위키미디어 커먼즈에는 압축 골절과 관련된 미디어가 있다. |
- Zeller, J. L.; Burke, A. E.; Glass, R. M. (2008). "Osteomyelitis". JAMA. 299 (7): 858. doi:10.1001/jama.299.7.858. PMID 18285597.
- 라이틱 병변에 관한 메디스케이프 기사
- 척수 전이 에메디컬 기사