포자니클라인
Pozanicline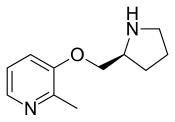 | |
| 식별자 | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS 번호 | |
| 펍켐 CID | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| 화학 및 물리적 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C11H16N2O |
| 어금질량 | 192.258 g·190−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
포자니클라인(INN,[1] codenamed ABT-089)은 아보트가 개발한 약물로, 비등방성 및 신경보호 효과가 있다.[2][3][4] 동물 연구는 그것이 ADHD의[5] 치료에 유용하다고 제안했고 이후 인간 실험은 ABT-089가 이 응용에 효과적이라는 것을 보여주었다.[6] αβ42 니코틴 아세틸콜린 수용체에 대한 높은 친화력 하위 유형 선택성과 결합하며,[7][8] αβ62 하위 유형에는 부분적인 작용이 있지만 니코틴에 익숙한 α7 및 αβ34 하위 유형은 없다. 특히 학급 내 다른 약물에 비해 부작용을 유발하는 경향이 낮아 임상 개발의 신나는 후보군으로 꼽힌다.[9][10]
합성
포자니클린은 2-메틸-3-하이드록시피리딘과 보크-L-프로리놀에서 탈수반응을 거쳐 프로리놀의[11] 질소원자를 분해하여 합성한다.
참조
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 62" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 257. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2017.
- ^ Lin NH, Gunn DE, Ryther KB, Garvey DS, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Decker MW, et al. (January 1997). "Structure-activity studies on 2-methyl-3-(2(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy) pyridine (ABT-089): an orally bioavailable 3-pyridyl ether nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand with cognition-enhancing properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 40 (3): 385–90. doi:10.1021/jm960233u. PMID 9022806.
- ^ Sullivan JP, Donnelly-Roberts D, Briggs CA, Anderson DJ, Gopalakrishnan M, Xue IC, et al. (October 1997). "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine]: I. A potent and selective cholinergic channel modulator with neuroprotective properties". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 283 (1): 235–46. PMID 9336329.
- ^ Decker MW, Bannon AW, Curzon P, Gunther KL, Brioni JD, Holladay MW, et al. (October 1997). "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 283 (1): 247–58. PMID 9336330.
- ^ Prendergast MA, Jackson WJ, Terry AV, Decker MW, Arneric SP, Buccafusco JJ (March 1998). "Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (-)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys". Psychopharmacology. 136 (1): 50–8. doi:10.1007/s002130050538. PMID 9537682. S2CID 20080069.
- ^ Wilens TE, Verlinden MH, Adler LA, Wozniak PJ, West SA (June 2006). "ABT-089, a neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonist, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: results of a pilot study". Biological Psychiatry. 59 (11): 1065–70. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.10.029. PMID 16499880. S2CID 24951969.
- ^ Marks MJ, Wageman CR, Grady SR, Gopalakrishnan M, Briggs CA (October 2009). "Selectivity of ABT-089 for alpha4beta2* and alpha6beta2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain". Biochemical Pharmacology. 78 (7): 795–802. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.05.022. PMC 2772152. PMID 19481067.
- ^ Anderson DJ, Malysz J, Grønlien JH, El Kouhen R, Håkerud M, Wetterstrand C, et al. (October 2009). "Stimulation of dopamine release by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands in rat brain slices correlates with the profile of high, but not low, sensitivity alpha4beta2 subunit combination". Biochemical Pharmacology. 78 (7): 844–51. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.024. PMID 19555668.
- ^ Rueter LE, Anderson DJ, Briggs CA, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Gintant GA, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. (2004). "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews. 10 (2): 167–82. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMC 6741767. PMID 15179445.
- ^ Wilens TE, Decker MW (October 2007). "Neuronal nicotinic receptor agonists for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: focus on cognition". Biochemical Pharmacology. 74 (8): 1212–23. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.002. PMC 2974320. PMID 17689498.
- ^ Rueter LE, Anderson DJ, Briggs CA, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Gintant GA, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. (2006). "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews. 10 (2): 167–82. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMC 6741767. PMID 15179445.


