꼬리 또는 극단값을 모형화하는 데 자주 사용되는 확률 분포의 집합
이 글은 일반화된 파레토 분포라고 하는 연속적인 분포의 특정 계열에 관한 것이다. 일반화된 Pareto 분포의 계층 구조는 Pareto 분포 를 참조하십시오. 일반화 파레토 분포 확률밀도함수
μ 0 {\displaystyle \mu =0} μ {\displaystyle \sigma } {\displaystyle \xi} 누적분포함수
매개변수 μ ∈ ∞ ∞ {\ displaystyle \mu \in (-\inflt ,\inflt )\,} 위치 실제 ) σ 0 ∞ {\ displaystyle \sigma \in (0,\infit )\,} 척도
ξ ∞ ∞ {\ displaystyle \xi \in (-\inflt ,\inflt )\,} 모양 지원 x ⩾ μ ( ξ ⩾ 0 ) {\displaystyle x\geqslant \mu \,\;(\xi \geqslant 0)}
μ ⩽ x ⩽ μ − σ / ξ ( ξ < 0 ) \displaystyle \mu \leqslant x\leqslant \mu -\basma /\xi \;(\xi <0)} PDF 1 σ ( 1 + ξ z ) − ( 1 / ξ + 1 ) {\displaystyle {\frac {1}{\proxma }}}}(1+\xi z)^{-(1/\xi +1)}}}}
여기서 z x {\ displaystyle z={\frac {x-\mu }{\ma}}} CDF 1 − ( 1 + ξ z ) − 1 / ξ {\displaystyle 1-(1+\xi z)^{-1/\xi }\,} 평균 μ + σ 1 − ξ ( ξ < 1 ) {\displaystyle \mu +{\frac {\becma }{1-\xi }\,\(\xi <1)} 중앙값 μ + σ ( 2 ξ − 1 ) ξ {\displaystyle \mu +{\frac {\becma (2^{\xi }-1)}{\xi }} 모드 μ \displaystyle \mu } 분산 σ 2 ( 1 − ξ ) 2 ( 1 − 2 ξ ) ( ξ < 1 / 2 ) {\displaystyle {\frac {\proxma ^{2}}:{(1-\xi )^{2}(1-2\xi )}\,\(\xi <1/2)} 왜도 2 ( 1 + ξ ) 1 − 2 ξ ( 1 − 3 ξ ) ( ξ < 1 / 3 ) {\displaystyle {\frac{2(+\xi ){\sqrt{1-2\xi }}{{(1-3\xi )}\,\;(\xi <1/3)} 엑스트라 쿠르토시스 3 ( 1 − 2 ξ ) ( 2 ξ 2 + ξ + 3 ) ( 1 − 3 ξ ) ( 1 − 4 ξ ) − 3 ( ξ < 1 / 4 ) {\displaystyle {\frac {3(1-2\xi)}(2\xi ^{2}+\xi +3)}{{1-3\(1-4\xi )},\;(\xi <1/4)} 엔트로피 통나무를 하다 ( σ ) + ξ + 1 {\displaystyle \log(\displayma )+\xi +1} MGF e θ μ ∑ j = 0 ∞ [ ( θ σ ) j ∏ k = 0 j ( 1 − k ξ ) ] , ( k ξ < 1 ) {\displaystyle e^{\theta \mu }\,\sum _{j=0}^{\frac {(\theta \sigma )^{j}{\prod _{k=0}^{j}}(1-k\xi <1)} CF e i t μ ∑ j = 0 ∞ [ ( i t σ ) j ∏ k = 0 j ( 1 − k ξ ) ] , ( k ξ < 1 ) {\displaystyle e^{it\mu }\,\sum _{j=0}^{\flac{{\prod}{{k=0}^{j}(1-k\xi )}\;(k\xi <1)} 모멘트의 방법 ξ = 1 2 ( 1 − ( E [ X ] − μ ) 2 V [ X ] ) {\displaystyle \xi ={\frac {1}{1}:{2}}: 왼쪽(1-{\frac {(E[X]-\mu )^{2}}:{V[X]}}}\오른쪽)} σ = ( E [ X ] − μ ) ( 1 − ξ ) {\displaystyle \sigma =(E[X]-\mu )(1-\xi )}
통계 에서 일반화된 파레토 분포 (GPD)는 연속 확률 분포 의 한 계열이다. 그것은 종종 다른 분포의 꼬리를 모형화하는 데 사용된다. 위치 μ {\displaystyle \mu }, σ {\displaystyle \sigma }, ξ {\displaystyle \xi } . [1] [2] [3] 일부 참조에서는 형상 모수를 κ ξ {\ displaystyle \kappa =-\xi \,} . [4]
정의 GPD의 표준 누적분포함수(cdf)는 다음과[5]
F ξ ( z ) = { 1 − ( 1 + ξ z ) − 1 / ξ 을 위해 ξ ≠ 0 , 1 − e − z 을 위해 ξ = 0. {\displaystyle F_{\xi }(z)={\begin{pase}1-\좌측(1+\xi z\오른쪽)^{-1/\xi }&{\text{}}}}}}}}}}{}\xi }0의 경우 \nech. \end{case}}} 여기서 지원은 0 z ≥ (\ displaystyle \xi \geq }) 0 displaystyle 0 \ leq -1/\xi }} 대한 0 (\ displaystytle \ leq -1 xi }) . 해당 확률밀도함수(pdf)는
f ξ ( z ) = { ( 1 + ξ z ) − ξ + 1 ξ 을 위해 ξ ≠ 0 , e − z 을 위해 ξ = 0. {\displaystyle f_{\xi }(z)={\base}(1+\xi z)^{-{-{\frac {\xi +1}{\xi }}}&{\text{}}}}}}}}}}}}{}\xi =0의 경우. \end{case}}} 특성화 관련 위치 척도 분포 계열은 인수 z μσ {\ displaystyle {\frac {x-\mu}{\sigma }}}}
The cumulative distribution function of X ∼ G P D ( μ , σ , ξ ) {\displaystyle X\sim GPD(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi )} μ ∈ R {\displaystyle \mu \in \mathbb {R} } σ > 0 {\displaystyle \sigma >0} ξ ∈ R {\displaystyle \xi \in \mathbb {R} }
F ( μ , σ , ξ ) ( x ) = { 1 − ( 1 + ξ ( x − μ ) σ ) − 1 / ξ 을 위해 ξ ≠ 0 , 1 − 생략하다 ( − x − μ σ ) 을 위해 ξ = 0 , {\displaystyle F_{(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi )}(x)={\begin{cases}1-\left(1+{\frac {\xi (x-\mu )}{\sigma }}\right)^{-1/\xi }&{\text{for }}\xi \neq 0,\\1-\exp \left(-{\frac {x-\mu }{\sigma }}\right)&{\text{for }}\xi =0,\end{cases}}} where the support of X {\displaystyle X} x ⩾ μ {\displaystyle x\geqslant \mu } ξ ⩾ 0 {\displaystyle \xi \geqslant 0\,} μ ⩽ x ⩽ μ − σ / ξ {\displaystyle \mu \leqslant x\leqslant \mu -\sigma /\xi } ξ < 0 {\displaystyle \xi <0}
X G D ( μ μ ξ 확률밀도함수 (pdf) {\displaystyle X\sim GPD(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi
f ( μ , σ , ξ ) ( x ) = 1 σ ( 1 + ξ ( x − μ ) σ ) ( − 1 ξ − 1 ) {\displaystyle f_{(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi )}(x)={\frac {1}{\sigma }}\left(1+{\frac {\xi (x-\mu )}{\sigma }}\right)^{\left(-{\frac {1}{\xi }}-1\right)}} 다시 μ μ [\displaystyle \ xi geqslant } μs x μs μs mu displaystyle \leqslant \mu \cslima /xi μs
pdf는 다음과 같은 미분방정식 의 해법이다.[citation needed
{ f ′ ( x ) ( − μ ξ + σ + ξ x ) + ( ξ + 1 ) f ( x ) = 0 , f ( 0 ) = ( 1 − μ ξ σ ) − 1 ξ − 1 σ } {\displaystyle \left\{{\begin{array}{l}f'(x)(-\mu \xi +\sigma +\xi x)+(\xi +1)f(x)=0,\\f(0)={\frac {\left(1-{\frac {\mu \xi }{\sigma }}\right)^{-{\frac {1}{\xi }}-1}}{\sigma }}\end{array}}\right\}} 특례 형상 ξ {\displaystyle \xi } μ {\displaystyle \mu } 지수 분포 와 동일하다. With shape ξ > 0 {\displaystyle \xi >0} μ = σ / ξ {\displaystyle \mu =\sigma /\xi } Pareto distribution with scale x m = σ / ξ {\displaystyle x_{m}=\sigma /\xi } α = 1 / ξ {\displaystyle \alpha =1/\xi } If X {\displaystyle X} ∼ {\displaystyle \sim } G P D {\displaystyle GPD} ( {\displaystyle (} μ = 0 {\displaystyle \mu =0} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } ) {\displaystyle )} Y = log ( X ) ∼ e x G P D ( σ , ξ ) {\displaystyle Y=\log(X)\sim exGPD(\sigma ,\ xi )} [ 1] (exGPD는 지수화된 일반화된 파레토 분포를 의미 한다.) GPD는 Burr 분포 와 유사하다. 일반화된 Pareto 랜덤 변수 생성 GPD 랜덤 변수 생성 U 가 (0, 1)에 균일하게 분포 되어 있는 경우,
X = μ + σ ( U − ξ − 1 ) ξ ∼ G P D ( μ , σ , ξ ≠ 0 ) {\displaystyle X=\mu +{\frac {\sigma(U^{-\xi }-1)}{\xi }}}{\xi }}\심 GPD(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi \neq 0)} 그리고
X = μ − σ ln ( U ) ∼ G P D ( μ , σ , ξ = 0 ) . \displaystyle X=\mu -\sigma \ln(U)\sim GPD(\mu ,\sigma ,\xi =0). } 두 공식 모두 cdf의 역순으로 구한다.
Matlab Statistics Toolbox에서는 "gprnd" 명령을 쉽게 사용하여 일반화된 Pareto 난수를 생성할 수 있다.
지수-감마 혼합물로서의 GPD GPD 랜덤 변수는 감마 분산 속도 매개변수와 함께 지수 랜덤 변수로 표현될 수도 있다.
X Λ ∼ E x p ( Λ ) \displaystyle X \Lambda \sim Exp(\Lambda )} 그리고
Λ ∼ G a m m a ( α , β ) \displaystyle \Lambda \sim Gamma(\alpha ,\beta )} 그때
X ∼ G P D ( ξ = 1 / α , σ = β / α ) {\displaystyle X\sim GPD(\xi =1/\alpha,\\sigma =\beta /\alpha )} 그러나, 감마 분포에 대한 모수가 0보다 커야 하므로ξ {\displaystyle \xi }.
지수 일반화 파레토 분포 지수 일반화된 Pareto 분포(exGPD) 다른 값 σ {\displaystyle \sigma \si and displaystyle xi } 대한 e D pdfdf . If X ∼ G P D {\displaystyle X\sim GPD} ( {\displaystyle (} μ = 0 {\displaystyle \mu =0} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } ) {\displaystyle )} Y = log ( X ) {\displaystyle Y=\log(X)} exponentiated generalized Pareto distribution Y {\displaystyle Y} {\displaystyle \sim } e x G P D displaystyle exGPD }({\ 【\ displaystyle \xi }).
The probability density function (pdf) of Y {\displaystyle Y} ∼ {\displaystyle \sim } e x G P D {\displaystyle exGPD} ( {\displaystyle (} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } ) ( σ > 0 ) {\displaystyle )\,\,(\sigma >0)}
g ( σ , ξ ) ( y ) = { e y σ ( 1 + ξ e y σ ) − 1 / ξ − 1 을 위해 ξ ≠ 0 , 1 σ e y − e y / σ 을 위해 ξ = 0 , {\displaystyle g_{(\sigma ,\xi )}(y)={\begin{cases}{\frac {e^{y}}{\sigma }}{\bigg (}1+{\frac {\xi e^{y}}{\sigma }}{\bigg )}^{-1/\xi -1}\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi \neq 0,\\{\frac {1}{\sigma }}e^{y-e^{y}/\sigma }\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi =0,\end{cases}}} where the support is − ∞ < y < ∞ {\displaystyle -\infty <y<\infty } ξ ≥ 0 {\displaystyle \xi \geq 0} − ∞ < y ≤ log ( − σ / ξ ) {\displaystyle -\infty <y\leq \log(-\sigma /\xi )} ξ < 0 {\displaystyle \xi <0}
모든 ξ {\displaystyle \xi log σ {\displaystyle \log \sigma } ▼ {\displaystyle \xi}
exGPD 는 모든 σ 0 {\displaystyle \sigma >0 } ∞ ξ <\displaystyle \infult xi infulty }) .
ξ {\displaystyle \ xi} x G D ( σ ξ {\displaystyle exGPD(\sigma ,\xi )} . 분산 displaystyle \xi . 빨간색 점선은 ξ {\displaystyle \xi =0 ψ ′ π 6 {\displaystyle \psi '(1)=\pi ^{2}/6} . Y e x G P D σ ξ displaystyle Y\sim exGPD(\sigma ,\xi )} 모멘트 생성 기능 은 다음과 같다
M Y ( s ) = E [ e s Y ] = { − 1 ξ ( − σ ξ ) s B ( s + 1 , − 1 / ξ ) 을 위해 s ∈ ( − 1 , ∞ ) , ξ < 0 , 1 ξ ( σ ξ ) s B ( s + 1 , 1 / ξ − s ) 을 위해 s ∈ ( − 1 , 1 / ξ ) , ξ > 0 , σ s Γ ( 1 + s ) 을 위해 s ∈ ( − 1 , ∞ ) , ξ = 0 , {\displaystyle M_{Y}s= E[e^{sY}]={\begin{경우}-{\frac{1}{\xi}}{\bigg(}-{\frac{\sigma}{\xi}}{\bigg)}(s+1,-1/\xi)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}};0,\\{\frac{1}{\xi}}{\bigg(}{\frac{\sigma}{\xi}}{\bigg)}(s+1,1/\xi -s)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}}(-1,1/\xi),\xi 을 s\in, 0,\\\sigma ^{s}\Gamma(1+s)\,\,\(-1,\infty),\xi<>s\in.,\,\,\ ,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}s\in (-1,\infty ),\xi =0,\end{cases}}} 여기 B b {\displaystyle B(a,b)} γ () {\displaystyle \Gamma (a)} 베타 함수 와 감마 함수 를 나타낸다
The expected value of Y {\displaystyle Y} ∼ {\displaystyle \sim } e x G P D {\displaystyle exGPD} ( {\displaystyle (} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } ) {\displaystyle )} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } digamma 기능 을 통해 {\displaystyle \xi}
E [ Y ] = { 통나무를 하다 ( − σ ξ ) + ψ ( 1 ) − ψ ( − 1 / ξ + 1 ) 을 위해 ξ < 0 , 통나무를 하다 ( σ ξ ) + ψ ( 1 ) − ψ ( 1 / ξ ) 을 위해 ξ > 0 , 통나무를 하다 σ + ψ ( 1 ) 을 위해 ξ = 0. {\displaystyle E[Y]={\begin{경우}\log){\bigg(}-{\frac{\sigma}{\xi}}{\bigg)}+\psi(1)-\psi(-1/\xi+1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}}\xi<>0,\\\log){\bigg(}{\frac{\sigma}{\xi}}{\bigg)}+\psi(1)-\psi(1/\xi)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}}\xi>0,\\\log \sigma +\psi(1.)\,\,\ ,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi =0. \end{case}}} ξ( ∞ ∞ {\displaystyle \xi \in(-\inflt ,\inflt )} 대해 σ {\displaystyle \log \sigma }
The variance of Y {\displaystyle Y} ∼ {\displaystyle \sim } e x G P D {\displaystyle exGPD} ( {\displaystyle (} σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } ) {\displaystyle )} ξ {\displaystyle \xi } polygamma function of order 1 (als o trigamma 함수 호출:
V a r [ Y ] = { ψ ′ ( 1 ) − ψ ′ ( − 1 / ξ + 1 ) 을 위해 ξ < 0 , ψ ′ ( 1 ) + ψ ′ ( 1 / ξ ) 을 위해 ξ > 0 , ψ ′ ( 1 ) 을 위해 ξ = 0. {\displaystyle Var[Y]={\begin{경우}\psi '(1)-\psi '(-1/\xi+1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}}\xi<>0,\\\psi '(1)+\psi '(1/\xi)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}}\xi>0,\\\psi '(1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{에}.}\xi) 0.\end{case}} ξ {\displaystyle \xi} π 2 6 ≈ 1.64434 {\displaystyle \psi pi ^{2 6\ 1.644934
Note that the roles of the scale parameter σ {\displaystyle \sigma } ξ {\displaystyle \xi } Y ∼ e x G P D ( σ , ξ ) {\displaystyle Y\sim exGPD(\sigma ,\xi )} ξ {\displaystyle \xi } X ∼ G P D σ ξ {\displaystyle X\sim GPD(\sigma ,\xi )} 2]. The roles of the two parameters are associated each other under X ∼ G P D ( μ = 0 , σ , ξ ) {\displaystyle X\sim GPD(\mu =0,\sigma ,\xi )} V a r ( X ) {\displaystyle Var(X)}
힐의 추정기 Assume that X 1 : n = ( X 1 , ⋯ , X n ) {\displaystyle X_{1:n}=(X_{1},\cdots ,X_{n})} n {\displaystyle n} heavy-tailed distribution F {\displaystyle F} 1 / ξ {\displaystyle 1/\ xi }( ξ {\displaystyle \xi } 구체적으로 말하면, 꼬리 분포는 다음과 같이 설명된다.
F ¯ ( x ) = 1 − F ( x ) = L ( x ) ⋅ x − 1 / ξ , 얼마간 ξ > 0 , 어디에 L 천천히 변화하는 기능이다. {\displaystyle {\bar{F}(x)=1-F(x)=L(x)\cdot x^{-1/\xi }}\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{}}}}}일부 }\xi >0,\,\,{\text{{{{}}}}}}}{\text{{}}}}}}}}}}}은 서서히 변화하는 기능이다. }}} 형상 모수 ξ{\displaystyle \xi} 특히 ξ {\displaystyle \xi} 극단값 이론 에 특히 관심이 있다.
F u {\ displaystyle F_{u}} Pickands–Balkema–de Haan theorem (Pickands, 1975; Balkema and de Haan, 1974) states that for a large class of underlying distribution functions F {\displaystyle F} u {\displaystyle u} F u {\displaystyle F_{u}} ξ {\displaystyle \xi} : GPD는 POT 접근방식에서 핵심적인 역할을 한다.
POT 방법론을 이용한 유명한 추정자는 힐의 추정기 다. 힐 평가기의 기술적 공식은 다음과 같다. For 1 ≤ i ≤ n {\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n} X ( i ) {\displaystyle X_{(i)}} i {\displaystyle i} X 1 , ⋯ , X n {\displaystyle X_{1},\cdots ,X_{n}} Hill's estimator (see page 190 of Reference 5 by Embrechts et al [3] ) based on the k {\ displaystyle k}
ξ ^ k 언덕 = ξ ^ k 언덕 ( X 1 : n ) = 1 k − 1 ∑ j = 1 k − 1 통나무를 하다 ( X ( j ) X ( k ) ) , 을 위해 2 ≤ k ≤ n . {\displaystyle {\widehat {\xi }_{k}^{\text{ 힐}}}={\widehat{\xi }}_{k}^{\text{ Hill}}(X_{1:n})={\frac {1}{k-1}}\sum _{j=1}^{k-1}\log {\bigg (}{\frac {X_{(j)}}{X_{(k)}}}{\bigg )},\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}2\leq k\leq n.} 실제로 힐 추정기는 다음과 같이 사용된다. 먼저 추정기 ^ Hill {\ displaystyle {\widehat {\xi }_{k}^{\text }} 힐}}} 정수 k { 2 ⋯, } {\displaystyle k\in \{2,\cdots,n {( k , ξ ^ Hill )}k displaysty \(k, widehat{xi_}}}}}}}{k^{ text . 힐}}}\}_{k=2}^{ }}}. 다음 {{{\ widehat{\xi }}^{k text{{ n }} Hill}}\}_{k=2}^{n}} k {\displaystyle k} ξ {\displaystyle \xi } X 1 , ⋯ , X n {\displaystyle X_{1},\cdots ,X_{n}} ape {\displaystyle \xi 4].
Hill Estimator ξ ^ Hill widehat {\xi }_{k}^{\text }} Hill}}} X 1 : n = ( X 1 , ⋯ , X n ) {\displaystyle X_{1:n}=(X_{1},\cdots ,X_{n})} Pickand's estimator ξ ^ k Pickand {\displaystyle {\widehat {\xi }}_{k}^{\text{Pickand}}} [5 ] .)
참고 항목 참조 ^ Coles, Stuart (2001-12-12). An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values ISBN 9781852334598 ^ Dargahi-Noubary, G. R. (1989). "On tail estimation: An improved method". Mathematical Geology . 21 (8): 829–842. doi :10.1007/BF00894450 . S2CID 122710961 . ^ Hosking, J. R. M.; Wallis, J. R. (1987). "Parameter and Quantile Estimation for the Generalized Pareto Distribution". Technometrics . 29 (3): 339–349. doi :10.2307/1269343 . JSTOR 1269343 . ^ Davison, A. C. (1984-09-30). "Modelling Excesses over High Thresholds, with an Application" . In de Oliveira, J. Tiago (ed.). Statistical Extremes and Applications . Kluwer. p. 462. ISBN 9789027718044 ^ Embrechts, Paul; Klüppelberg, Claudia ; Mikosch, Thomas (1997-01-01). Modelling extremal events for insurance and finance ISBN 9783540609315
추가 읽기 Pickands, James (1975). "Statistical inference using extreme order statistics" . Annals of Statistics . 3 s : 119–131. doi :10.1214/aos/1176343003 Balkema, A.; De Haan, Laurens (1974). "Residual life time at great age" . Annals of Probability . 2 (5): 792–804. doi :10.1214/aop/1176996548 Lee, Seyoon; Kim, J.H.K. (2018). "Exponentiated generalized Pareto distribution:Properties and applications towards extreme value theory". Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods . 48 (8): 1–25. arXiv :1708.01686 doi :10.1080/03610926.2018.1441418 . S2CID 88514574 . N. L. Johnson; S. Kotz; N. Balakrishnan (1994). Continuous Univariate Distributions Volume 1, second edition . New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-58495-7 Barry C. Arnold (2011). "Chapter 7: Pareto and Generalized Pareto Distributions" . In Duangkamon Chotikapanich (ed.). Modeling Distributions and Lorenz Curves . New York: Springer. ISBN 9780387727967 Arnold, B. C.; Laguna, L. (1977). On generalized Pareto distributions with applications to income data . Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University, Department of Economics. 외부 링크
이산형 일변도의
연속 일변도의
의 지지를 받고 있는. 경계 간격 의 지지를 받고 있는. 반무한 간격을 두고 지지의 대체로 실선 지지하여 누구의 타입이 다른가.
혼합 일변도의
다변량 (공동) 방향 퇴보하다 그리고 단수 가족들
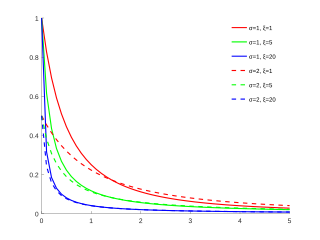

 대한 GPD 분포 함수 및
대한 GPD 분포 함수 및  (와)
(와) 













![{\displaystyle e^{\theta \mu }\,\sum _{j=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(\theta \sigma )^{j}}{\prod _{k=0}^{j}(1-k\xi )}}\right],\;(k\xi <1)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/41cf9f358ac58dcba4130cba492879256576e783)
![{\displaystyle e^{it\mu }\,\sum _{j=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(it\sigma )^{j}}{\prod _{k=0}^{j}(1-k\xi )}}\right],\;(k\xi <1)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/53bfef161abce3834ebc5908620389e3174d612f)
![{\displaystyle \xi ={\frac {1}{2}}\left(1-{\frac {(E[X]-\mu )^{2}}{V[X]}}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/029894dab6a61a875e17d8ee5f27c7fe52dc4a89)
![{\displaystyle \sigma =(E[X]-\mu )(1-\xi )}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7ae5aff7c32202ca44e85df4abac26bc3e6deb14)




 ,
, 


































 displaystyle \sigma },
displaystyle \sigma },









![{\displaystyle M_{Y}(s)=E[e^{sY}]={\begin{cases}-{\frac {1}{\xi }}{\bigg (}-{\frac {\sigma }{\xi }}{\bigg )}^{s}B(s+1,-1/\xi )\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}s\in (-1,\infty ),\xi <0,\\{\frac {1}{\xi }}{\bigg (}{\frac {\sigma }{\xi }}{\bigg )}^{s}B(s+1,1/\xi -s)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}s\in (-1,1/\xi ),\xi >0,\\\sigma ^{s}\Gamma (1+s)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}s\in (-1,\infty ),\xi =0,\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/28884f7453a08deb806e6dcfadd72715427ba40b)


![{\displaystyle E[Y]={\begin{cases}\log \ {\bigg (}-{\frac {\sigma }{\xi }}{\bigg )}+\psi (1)-\psi (-1/\xi +1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi <0,\\\log \ {\bigg (}{\frac {\sigma }{\xi }}{\bigg )}+\psi (1)-\psi (1/\xi )\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi >0,\\\log \sigma +\psi (1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi =0.\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a8417be06df13f42af281e304598ef2e687d03b5)


![{\displaystyle Var[Y]={\begin{cases}\psi '(1)-\psi '(-1/\xi +1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi <0,\\\psi '(1)+\psi '(1/\xi )\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi >0,\\\psi '(1)\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\text{for }}\xi =0.\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b3d91dba75f48dfd9845bc57efdc32455bacac8a)


















 순서 쌍
순서 쌍




